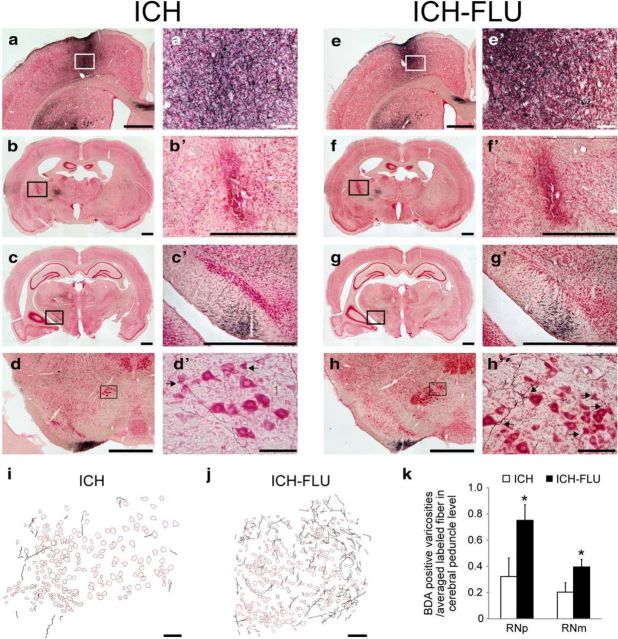
Figure 4.
Axonal projections from the ipsilesional forelimb motor cortex after ICH and ICH-FLU. To characterize the anatomical reorganization of the ipsilesional forelimb area, anterograde tracing assay using BDA was conducted. a′–h′ show a higher magnification of a–h. a, e, Injection site of BDA in the ipsilesional motor cortex forelimb area. b, f, ICH lesion site. Most of the lesions caused by ICH were located in the IC and some intact corticofugal fibers still remained around the lesion. c, g, BDA-positive fibers running through the cerebral peduncle. d, h, Red nucleus (magnocellular part). Compared with the ICH group (d′), many BDA-labeled fibers were observed around the ipsilesional red nucleus in the ICH-FLU group (h′). Arrows indicate boutons along axons contacting large-sized red nucleus neurons. i, j, Camera lucida drawing of the BDA-positive axons in the red nucleus. k, Quantitative analysis for the boutons of the cortico-rubral axons. The number of BDA-positive boutons in the RNp and RNm normalized by the total number of labeled axons was significantly higher in the ICH-FLU group than in the ICH group. Scale bar, 1000 μm for a–h, c′, and g′; 500 μm for b′ and f′; 100 μm for a′, d′, e′, h′, i and j. *p < 0.05 vs ICH. Values are shown as mean ± SEM.