Table 1.
A list of parameters used to measure arterial stiffness.
| Definition (unit) | Formula | Notes |
| Pressure-strain modulus, Eρ (Pa) |
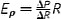
|
R can also be replaced with diameter (D). Extrinsic mechanical property |
| Elastic modulus, E (Pa) |
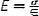
|
The slope of stress-strain (σ − ε) curve, assuming linear homogenous, incompressible wall material. Thin-wall or thick-wall assumptions lead to different calculations of σ and ε. Intrinsic material property |
| Incremental elastic modulus (1), E inc (Pa) |
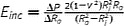
|
R o and R i are external and internal radii and can be replaced with corresponding diameters (D). Assuming locally linear, homogenous, incompressible (if ν = 0.5) wall material. Thick wall assumption. Intrinsic material property |
| Incremental elastic modulus (2), E inc (Pa) |
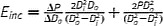
|
Modified E inc assuming orthotropic cylindrical tube. Intrinsic material property |
| Stiffness constant, β (dimensionless) |
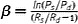
|
P s and P d are systolic and diastolic pressures. Radius R can be replaced with diameter (D). Assume homogenous, incompressible, isotropic material. Extrinsic mechanical property |
| Distensibility, D, (1/Pa) |
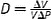
|
V (volume) can be replaced with A (area). Extrinsic mechanical property |
| Compliance, C, (m 3/Pa) |
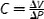
|
V (volume) can be replaced with A (area). Extrinsic mechanical property |
P = pressure, R = radius, D = diameter, V = volume, A = area. Adapted from Wang Z, Chesler NC. Pulmonary vascular wall stiffness: An important contributor to the increased right ventricular afterload with pulmonary hypertension. Pulm Circ. 2011;1(2):212–223.
