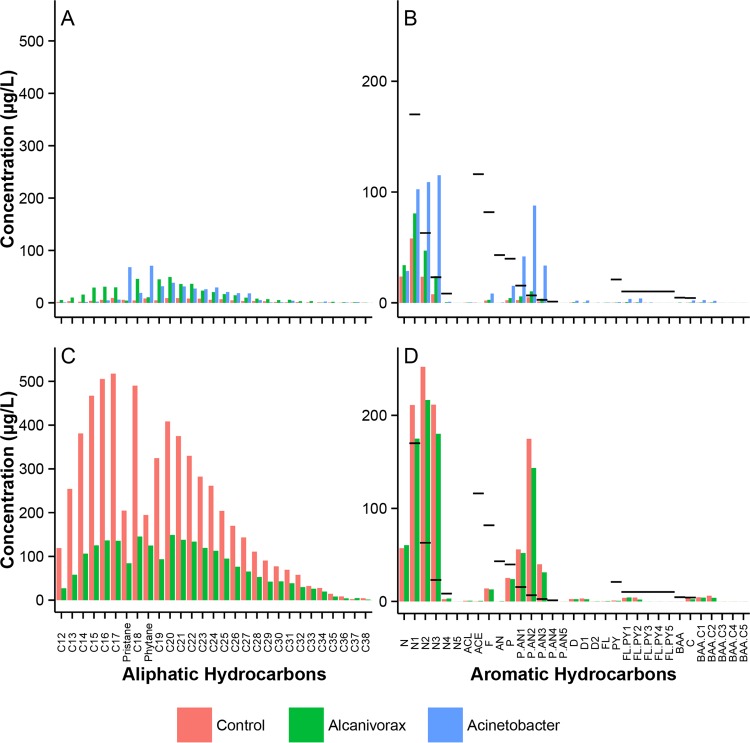
FIG 4.
Detailed analysis of aliphatic (A and C) and aromatic (B and D) hydrocarbons present in the WAF from the crude oil treatment (A and B) or the CEWAF from the dispersed-oil treatment (C and D). Acinetobacter-treated dispersed-oil samples were excluded from this figure due to extraction difficulties in separating EPS from hydrocarbons. EPA acute potency divisor values for aromatic hydrocarbons are indicated on graphs B and D by black bars. Data shown were collected after 7 days of incubation. See the supplemental material for an expanded version of this figure. Target PAHs are as follows: N and NC1-C4, naphthalene and alkylated homologues; ACL, acenaphthylene; ACE, acenaphthene; F, fluorene; D and DC1-C2, dibenzothiophene and alkylated homologues; P, AN, and P/ANC1-C4, phenanthrene, anthracene, and their alkylated homologues; FL, PY, and FL/PYC1-C4, fluoranthene, pyrene, and their alkylated homologues; BAA, C, and BAA/CC1-C4, benz[a]anthracene, chrysene, and their alkylated homologues; BBF, BKF, BAP, DA, and BP/PERC1-C4, benzo[b]fluoranthene, benzo[k]fluoranthene, benzo[a]pyrene, dibenz[a,h]anthracene, and alkylated homologues; ID, indeno[1,2,3-cd]pyrene; and BGP, benzo[ghi]perylene.