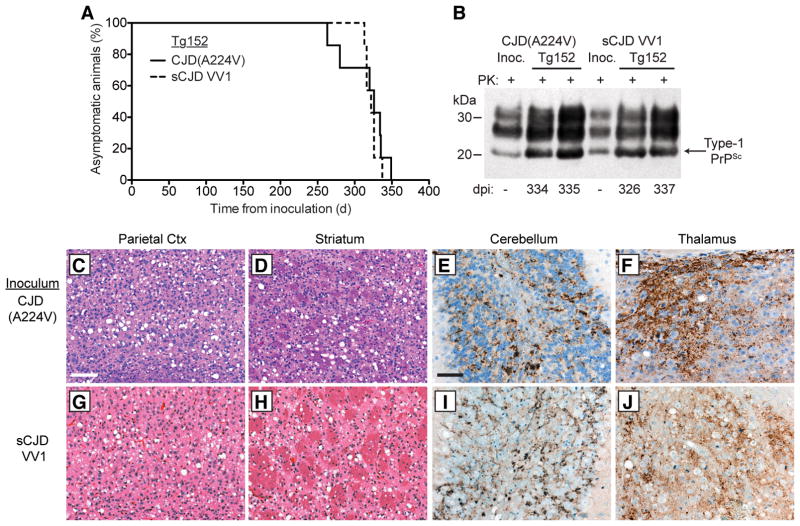
Figure 2. Transmission of CJD(A224V) to transgenic mice.
(A) Kaplan-Meier survival curves for Tg(HuPrP,V129)152 mice inoculated with brain homogenate from either the CJD(A224V) patient (solid black line, n = 7) or an sCJD VV1 patient (dashed black line, n = 7). The curves were not significantly different by the Log-rank test (P = 0.56). (B) Immunoblot of PK-resistant PrPSc in the brains of clinically ill Tg152 mice at the indicated days postinoculation (dpi) with either CJD(A224V) or sCJD VV1 brain homogenate. PrPSc profiles in the human brain homogenates used for inoculation (“Inoc.”) are shown for comparison. PK-resistant PrP was detected using the antibody HuM-P. (C–J) Neuropathological characterization of CJD-inoculated Tg152 mice. Brain sections from clinically ill mice at 313–337 dpi with either CJD(A224V) (C–F) or sCJD VV1 (G–J) brain homogenate were analyzed by H&E staining (C, D, G, and H) or by immunostaining for PrP (E, F, I, and J). Prominent spongiform degeneration was observed in the parietal cortex (C, G) and striatum (D, H), and abundant granular PrPSc deposition was observed in the granule cell layer of the cerebellum (E, I) as well as the thalamus (F, J). PrPSc deposits were visualized using the antibody 3F4. Scale bar in C represents 100 μm and also applies to panels D, G, and H; scale bar in E represents 50 μm and also applies to panels F, I, and J.