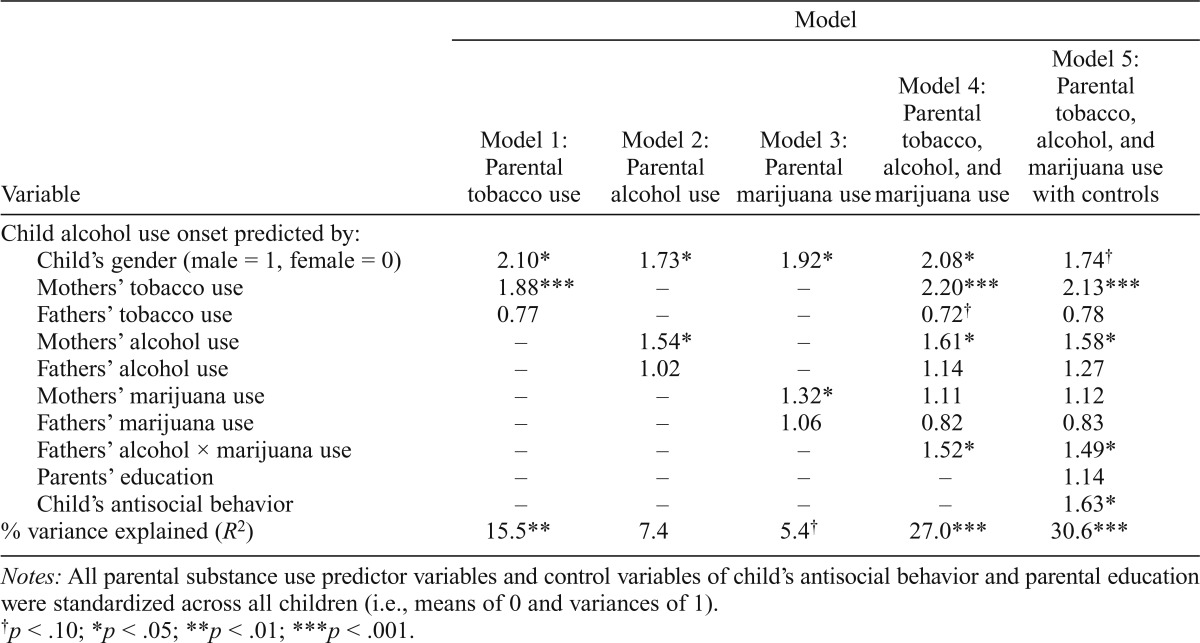
Table 2.
Predicted probability of child alcohol use onset given the predictor variables and percentage of overall variance explained from the survival analyses
| Variable | Model |
||||
| Model 1: Parental tobacco use | Model 2: Parental alcohol use | Model 3: Parental marijuana use | Model 4: Parental tobacco, alcohol, and marijuana use | Model 5: Parental tobacco, alcohol, and marijuana use with controls | |
| Child alcohol use onset predicted by: Child’s gender (male = 1, female = 0) | 2.10* | 1.73* | 1.92* | 2.08* | 1.741 |
| Mothers’ tobacco use | 1.88*** | – | – | 2.20*** | 2.13*** |
| Fathers’ tobacco use | 0.77 | – | – | 0.721 | 0.78 |
| Mothers’ alcohol use | – | 1.54* | – | 1.61* | 1.58* |
| Fathers’ alcohol use | – | 1.02 | – | 1.14 | 1.27 |
| Mothers’ marijuana use | – | – | 1.32* | 1.11 | 1.12 |
| Fathers’ marijuana use | – | – | 1.06 | 0.82 | 0.83 |
| Fathers’ alcohol × marijuana use | – | – | – | 1.52* | 1.49* |
| Parents’ education | – | – | – | – | 1.14 |
| Child’s antisocial behavior | – | – | – | – | 1.63* |
| % variance explained (R2) | 15.5** | 7.4 | 5.4t | 27.0*** | 30.6*** |
Notes: All parental substance use predictor variables and control variables of child’s antisocial behavior and parental education were standardized across all children (i.e., means of 0 and variances of 1).
p < .10;
p < .05;
p < .01;
p < .001.