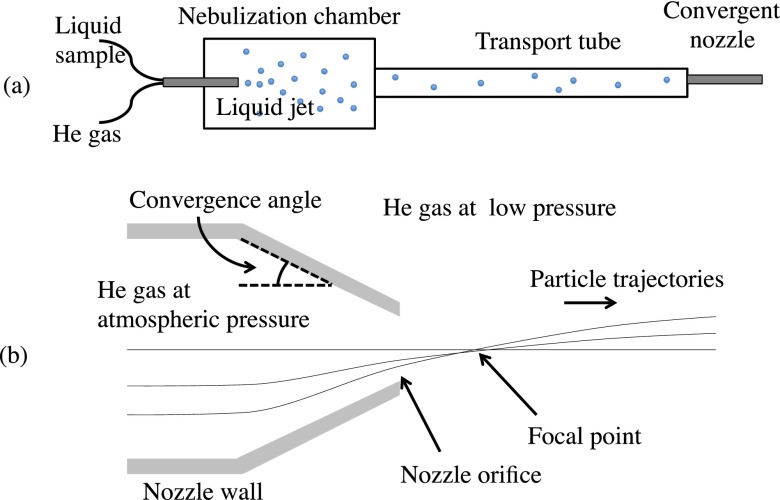
FIG. 1.
(a) Schematic of the aerosol injector assembly and convergent nozzle. Liquid drops are formed in a nebulization chamber via a gas-dynamic virtual nozzle, which then pass through a transport tube before reaching the convergent nozzle depicted in (b). Particle trajectories closely follow the gas streamlines within the convergent nozzle, which is at near-atmospheric pressure. Upon exiting the nozzle, the pressure suddenly drops, and the ejected high-speed particles follow nearly straight-line trajectories, though they may accelerate slightly upon exiting. All particles cross over the nozzle's axis of symmetry at a common focal point that varies only slightly with the initial position of the particles at the exit orifice. The slightly curved trajectories of particles exiting the nozzle are exaggerated for illustrative purposes.