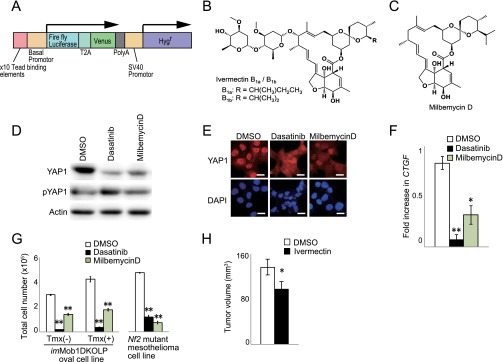
Fig. S6.
Identification of inhibitory effect on YAP1 activity of two antiparasitic macrocyclic lactones. (A) Schematic diagram of the reporter DNA construct that was transfected into H1299 cells to measure YAP1 activity. The construct contains 10 copies of the TEAD-binding element from the CTGF gene, firefly luciferase, and the Venus and Hygr sequences. A control DNA construct containing renilla luciferase and Neor (not shown) was cotransfected into cells to facilitate sensitive screening of compounds for their ability to inhibit YAP1 activity. (B and C) Chemical structures of positive screen “hits” ivermectin (B) and milbemycin D (C), which are antiparasitic macrocyclic lactone derivatives. (D and E) H1299 cells were treated with DMSO (vehicle), dasatinib (positive control), or milbemycin D for 24 h. (D) Immunoblot to detect YAP1 and pYAP1. Actin, loading control. (E) Immunostaining to detect total YAP1 protein (red). DAPI (blue), nuclei. (Scale bars, 20 μm.) (F) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of expression of the YAP1 downstream effector CTGF in the H1299 cells in D and E. Data are the mean ± SEM (n = 3). (G) Quantitation of total cell numbers in cultures of imMob1DKOLP ± Tmx cells and NCI-H290 Nf2-deficient human mesothelioma cells treated with vehicle (DMSO), dasatinib (0.5 μM), or milbemycin D (10 µM) for 3 d. Tmx was administered 5 d before treatment with agents. Data are the mean ± SEM (n = 3). For all panels, data shown are representative of at least three trials. *P < 0.05. **P < 0.01. (H) Quantitation of tumor growth in nude mice that were xenografted with imMob1DKOLP+Tmx cells and treated with vehicle (n = 40 mice) or ivermectin (n = 36) for 22 d. Data are the mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05.