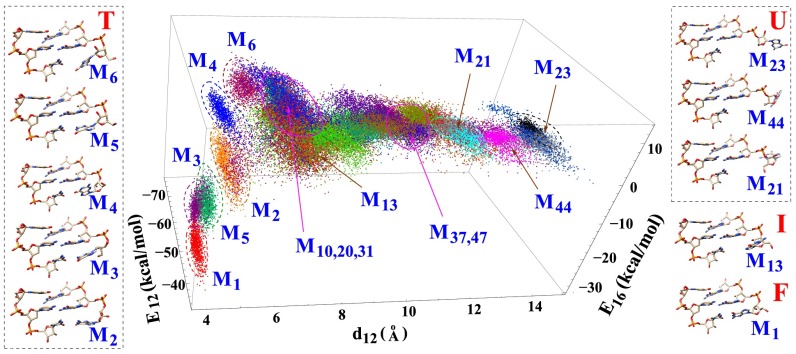
Fig. 2.
Order parameters used to classify conformations: is the distance between the geometric centers of heavy atoms between the G1 and G2 bases, and and are the nonbonded interactions (van der Waals and electrostatic energies given by VMD) between nucleotides G1 and G2 and between nucleotides G1 and C6, respectively. These energies characterize the base stacking and pairing interactions. The figure shows 1,000 randomly selected structures for each cluster. Ten centroid structures are shown for illustration. M1 is the native folded structure. M21, M23, and M44 are the unfolded structures with large . Other structures are partially folded or misfolded structures. M2, M3, and M5 have strong base stacking () and pairing () interactions. M4 and M13 have native-like backbone conformations, especially for the sugar ring atoms, but a partially unfolded base orientation. M6 has nonnative conformations for both the base and the backbone of nucleotide G1. The magenta circles indicate the order parameters for the transition states. Structures of the other clusters, as well as the other order parameters, are shown in SI Appendix.