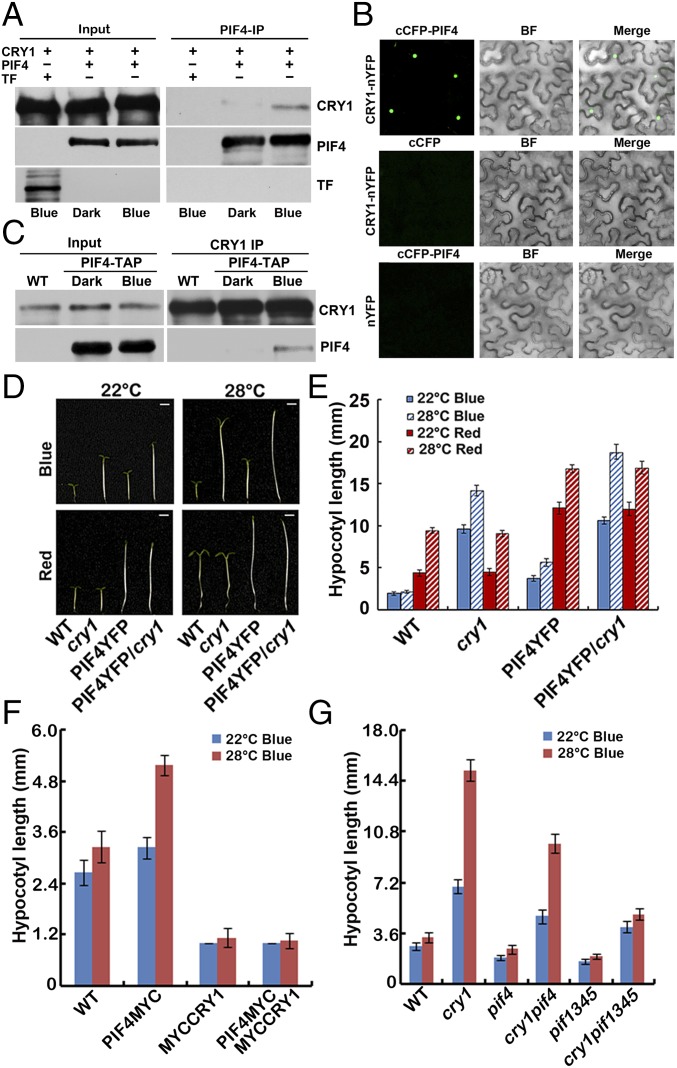
Fig. 2.
CRY1 interacts with PIF4 in a blue light-dependent manner. (A) In vitro pull-down assays showing blue light-dependent interaction between CRY1 and PIF4. His-TF–tagged PIF4 or His-TF tag were mixed with CRY1 expressed and purified from insect cells (sf9) in the dark condition, and were incubated under blue light (40 μmol⋅m−2⋅sec−1) or dark conditions for 30 min, and PIF4 antibody was used for the in vitro pulldown. The products were analyzed by immunoblot probed with the anti-CRY1 (CRY1) or the anti-PIF4 antibody (PIF4) or the anti-His antibody (TF). (B) BiFC assays of the in vivo protein interaction. Leaf epidermal cells of Nicotiana benthamiana were cotransformated with cCFP-PIF4 and CRY1-nYFP or cCFP and CRY1-nYFP or nYFP and cCFP-PIF4. BF, bright field. Merge, overlay of the YFP and bright-field images. (C) Co-IP assays of samples prepared from 6-d-old 35S::PIF4-TAP seedlings grown in long-day condition (16 light/8 dark), moved to dark for 1 d, then either exposed to blue light (40 μmol⋅m−2⋅sec−1) or kept in dark. Total proteins (input) or IP product of anti-CRY1 antibody (CRY1-IP) were probed, in immunoblots, by the anti-CRY1 antibody (CRY1), stripped, and reprobed by the anti-MYC (PIF4-TAP) antibody. (D–G) Phenotypic analysis. (D and E) Seedlings of the indicated genotypes were grown in the 22 °C or 28 °C continuous blue or red light (both 40 μmol⋅m−2⋅sec−1) for 4 d. (F and G) Seedlings of the indicated genotypes were grown in the 22 °C or 28 °C continuous blue light (40 μmol⋅m−2⋅sec−1) for 4 d. The hypocotyl lengths of the indicated genotypes were measured and are shown in F and G. SDs (n > 15) are indicated.