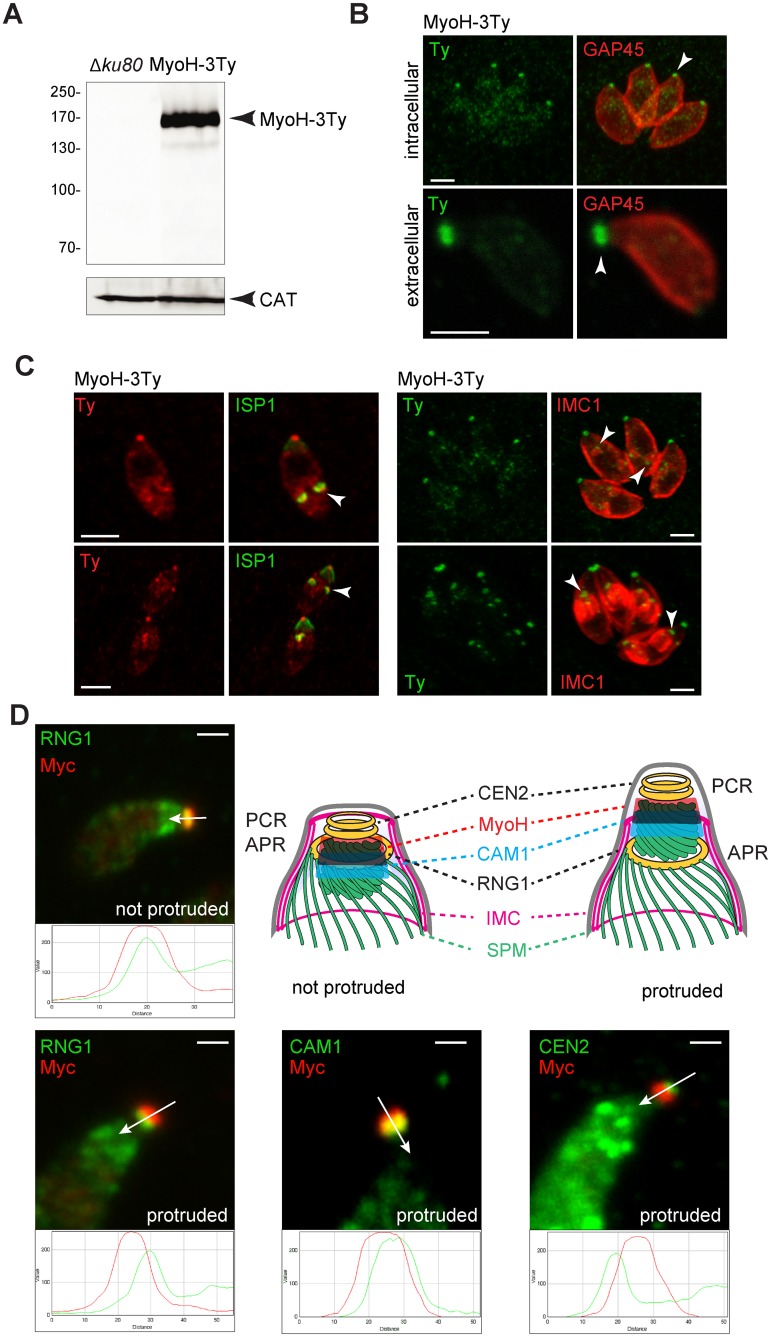
Fig 1. T. gondii myosin H appears during IMC formation and localizes close to the pre-conoidal rings.
(A) TgMyoH-3Ty is found at the predicted molecular weight by western blot (174 kDa). T. gondii catalase (CAT) was used as loading control. (B) MyoH-3Ty localizes at the extremities of the conoid in intra- (upper panel) and extracellular parasites (lower panel) (arrowhead). GAP45 stains the periphery of the parasites. Scale bar 2 μm. (C) MyoH-Ty localization during parasite division using respectively the IMC sub-compartment protein 1 (ISP1) and the inner membrane complex 1 (IMC1) markers. MyoH (arrowhead) appears early during division and accumulates at the apical end of the newly formed parasites. Scale bar 2 μm. (D) The precise localization of MycMyoH relatively to the conoid markers: RING1 (RNG1) at the apical polar ring (APR); calmodulin 1 (CAM1) in the middle part of the conoid and centrin 2 (CEN2) at the pre-conoidal rings (PCR). Co-localizations are assessed by the RGB profile plots determined using ImageJ along the arrows. Conoid protrusion in extracellular parasites was induced with A23187. IMC: inner membrane complex, SPM: subpellicular microtubules. Scale bar 1 μm.