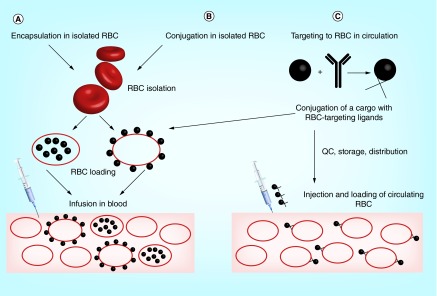
Figure 1. . Strategies for drug delivery by red blood cells.
Two approaches involve isolation of RBC (either from patient's autologous blood or from a donor blood), followed by drug loading using encapsulation or surface conjugation and injection of RBC-drug complex in the bloodstream (A & B). In the third approach (C), drug loading can be performed either in vivo by injecting the RBC-targeted drugs in bloodstream (thereby providing a homogenous loading on circulating RBC), or in vitro as a one-step modification of strategy B.
RBC: Red blood cell; QC: Quality control.