Figure 3.
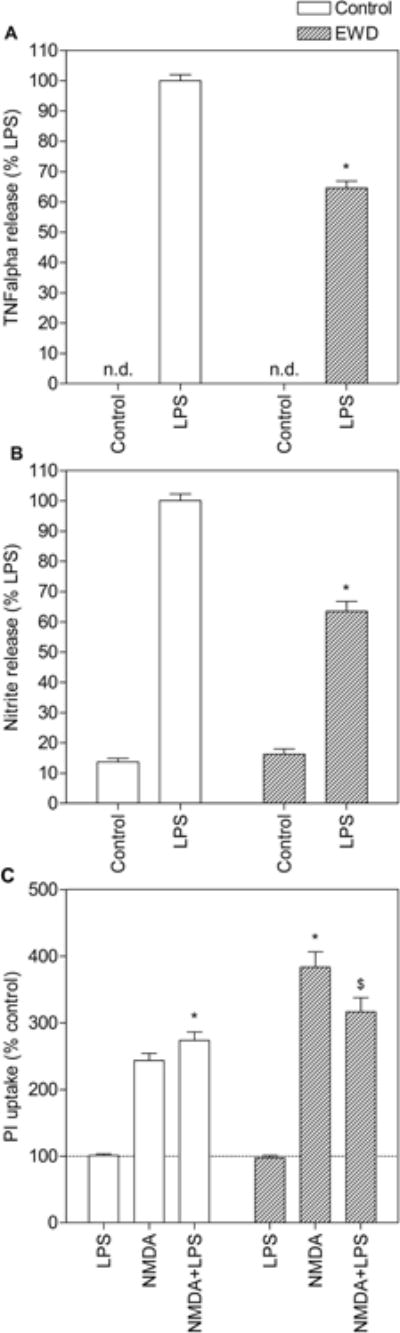
Effects of ethanol withdrawal (EWD) on proinflammatory release and toxicity induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and/or N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) in organotypic hippocampal cultures. Slices were treated with LPS and/or NMDA under control conditions (empty bars) and during EWD (dashed bars). Culture media was collected after 24h and assayed for TNF-alpha (A) and NO (B) content following PI uptake measurement (C). For (A) and (B), *p<0.001 compared to LPS alone. Data are expressed as percent release induced by LPS alone (means ± SEM). n > 27 hippocampal slices from 2 independent experiments for each treatment group. For (C), *p<0.05 compared to NMDA alone; $p<0.01 compared to NMDA+EWD. Data are expressed as percent of untreated control (means ± SEM). Dotted line represents untreated control. n > 117 hippocampal slices from 5 independent experiments for each treatment group.
