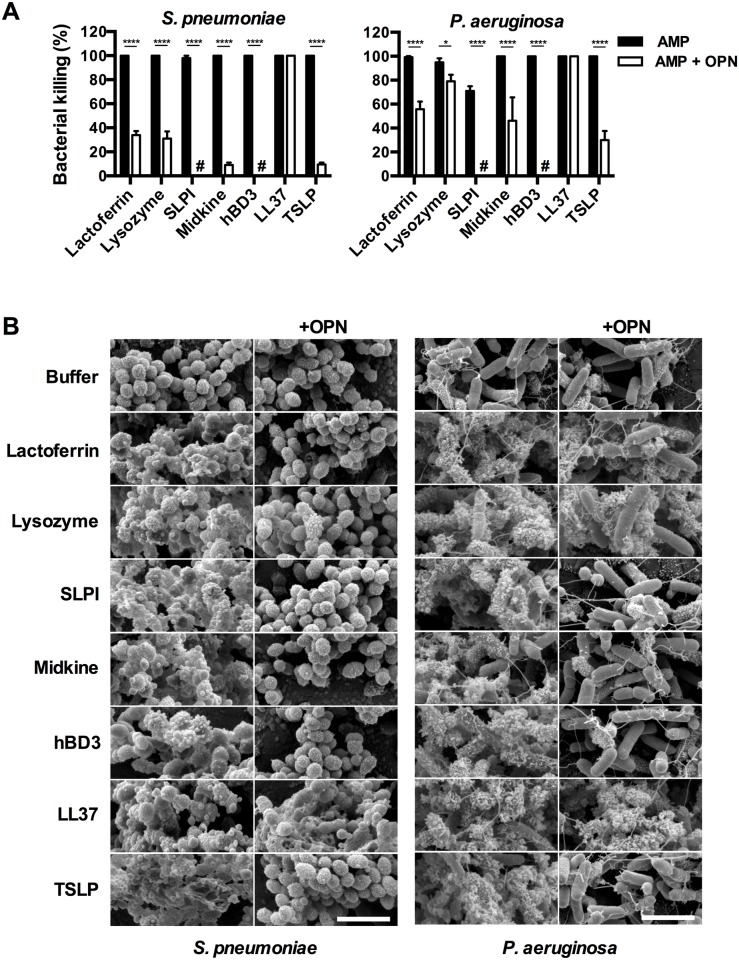
Fig 3. OPN impairs the bactericidal activity of AMPs.
(A) Interference of OPN with the bactericidal activity of AMPs was investigated using viable counts with S. pneumoniae and P. aeruginosa. Bacteria were grown to mid-logarithmic phase and incubated with AMPs alone (3 μM) or AMPs pre-incubated with OPN at ratio of 1:1 for one hour at 37°C. OPN caused inhibition of the bactericidal activity of all AMPs investigated except for LL-37. The histograms represent mean and standard deviation from three separate experiments. Two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test was used for statistical analysis. *P≤0.05, and ****P ≤ 0.0001. (B) Scanning electron microscopy images shows the morphology of bacteria after incubation with AMPs alone or AMPs pre-incubated with OPN (1:1). The AMPs alone permeabilized the membrane and caused leakage of intracellular contents indicating killing of the bacteria, which was confirmed in a parallel viable counts assay. Upon co-incubation of AMPs and OPN, the bacteria remained intact, except in the case of LL-37 and to some extent in the cases of P. aeruginosa (OPN with lactoferrin, lysozyme, and midkine). The scale bars in bottom figures in the right panels are 5 μm.