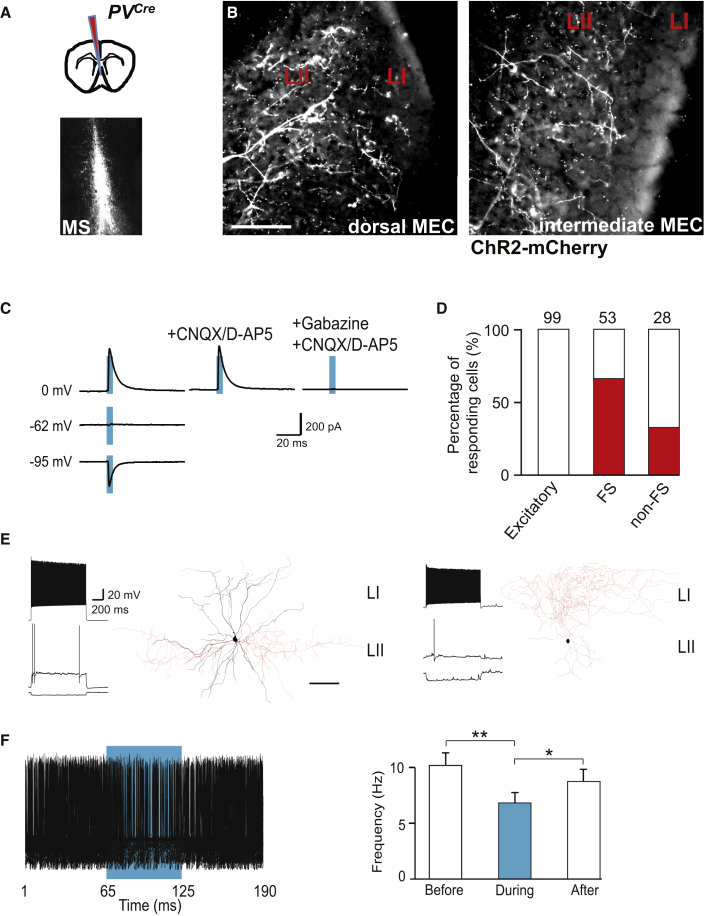
Figure 7.
Septal PV+ Neurons Inhibit Preferentially FS Interneurons in LII of the MEC
(A) Schematic drawing indicating the site of virus injection into the MS (top). MCherry expression following AAV DIO ChR2-mCherry injection into the MS of a PVCre mouse (coronal section; bottom).
(B) ChR2-mCherry+ axons in LII of the dorsal (left) and intermediate (right) MEC (sagittal sections). Scale bar, 50 μm.
(C) Responses of a targeted FS cell in MEC LII at the indicated potentials and in the presence of indicated antagonists. Blue bars show the duration of laser pulses.
(D) Histogram indicating percentage of responding neurons (red) in LII. The numbers above the bars indicate the number of analyzed cells.
(E) Representative firing pattern and reconstruction of a targeted FS (left) and a targeted non-FS GABAergic neuron (right). Dendrites are indicated in black and axons in red. Scale bar, 100 μm.
(F) Stimulation of septal PV+ long-range projections reduced spiking in LII FS neurons. Responding cells were depolarized to suprathreshold potentials, and long-range axons were stimulated with 60-ms pulses at 8 Hz. Superimposed traces of a representative cell (left) and histogram (right) showing significant reduction of the firing rate during 60-ms pulses (∗p < 0.05 and ∗∗p < 0.01). Data represent mean ± SEM.
Abbreviations are as follows: L, layer; MEC, medial entorhinal cortex; MS, medial septum; FS, fast-spiking interneuron; non-FS, non-fast-spiking interneuron; and PV, parvalbumin. See also Figures S7 and S8.