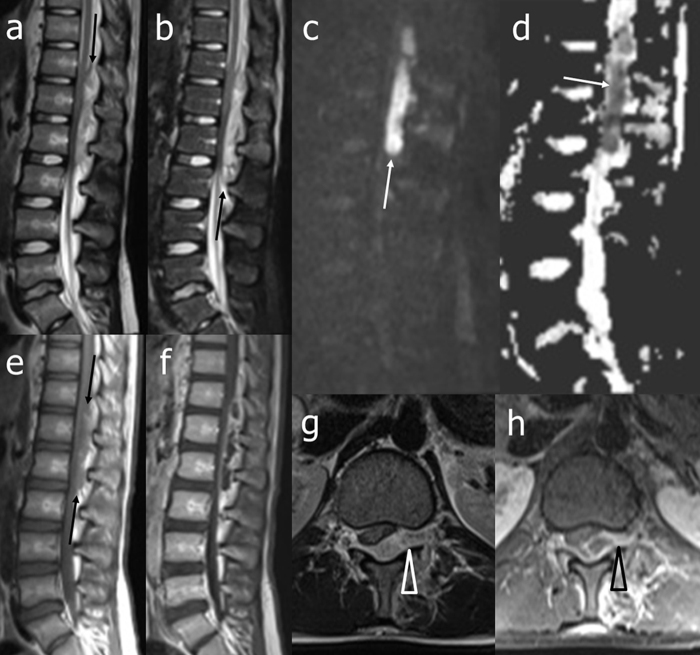
Fig. 1.
Magnetic resonance imaging of the thoraco-lumbar spine at diagnosis: unenhanced T2-weighted (a), short tau inversion recovery (STIR) (b), diffusion-weighted (DW) (c), apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) map (d), and T1-weighted (e) sagittal and T2-weighted axial (g) images, and gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted sagittal (f) and axial (h) images. At the thoracolumbar junction, a posterior median-left paramedian epidural collection compressing the caudal spinal cord, conus medullaris, and upper cauda equina is clearly evident. The lesion shows irregular signal intensity on unenhanced conventional sequences (a, b, and e, black arrows), restricted diffusion on DW images and ADC map (c, d, white arrows), and peripheral gadolinium-enhancement (f, h). Note also that the lesion shows extent toward the left intervertebral foramen (g, h, arrow head). STIR image does not show associated abnormal signal intensity of the bone marrow.