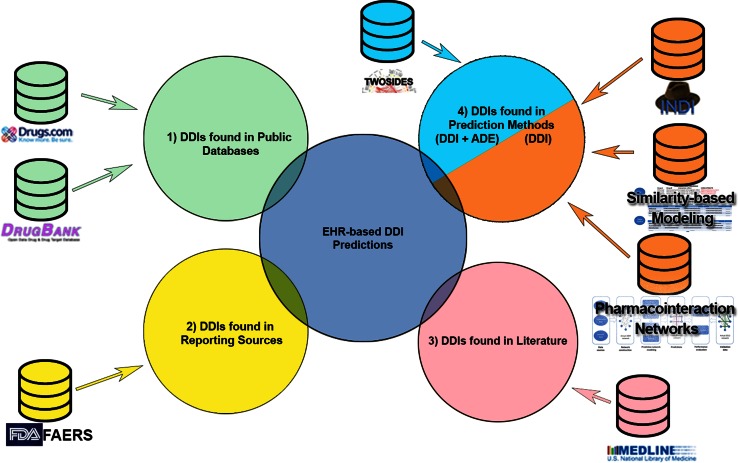
Fig. 1.
Overview of sources used for prioritizing drug–drug-event associations. EHR-derived associations are used as input to search existing evidence sources (1–3), and to assess support from previously developed DDI prediction methods (4). We group the information and DDI prediction methods into 1 public databases (green)—used for filtering out known associations; 2 official sources of drug adverse event reports (yellow); 3 biomedical literature (pink); and lastly 4 non-EHR-based DDI prediction methods. For each evidence type, we also show the specific sources we used and methods implemented, respectively. Only one of the four DDI prediction methods (TWOSIDES) associates predicted interactions with ADEs (cyan). The other three methods predict drug–drug interactions without an accompanying ADE (orange). ADE adverse drug event, DDI drug–drug interaction, EHR electronic health records