Figure 6.
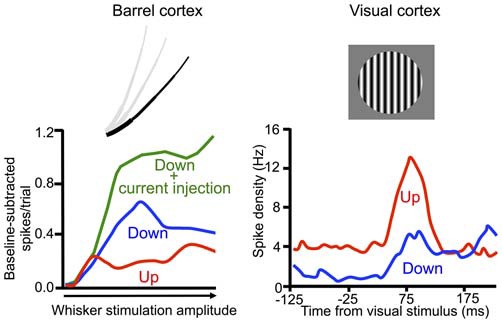
Up states differentially affect sensory-evoked responses of cortical neurons in barrel and visual cortex. (Left) In rat barrel cortex, whisker stimulation evokes a proportionally larger spiking output during the Down state compared to the Up state. Decreased driving force due to depolarization during the Up state is unlikely to explain this effect since it is not seen with depolarizing current injection during the Down state. Network effects (e.g., thalamocortical synaptic depression or increased intracortical synaptic inhibition) are more likely to account for reduced responsiveness in barrel cortex neurons during the Up state compared to the Down state. (Right) Conversely, in cat visual cortex, drifting-grating stimuli evoke larger spiking output during Up states compared to Down states. Left adapted by permission from the Society for Neuroscience: Journal of Neuroscience (Hasenstaub et al., 2007), © 2007. Right adapted by permission from the American Physiological Society: Journal of Neurophysiology (Haider et al., 2007), © 2007.
