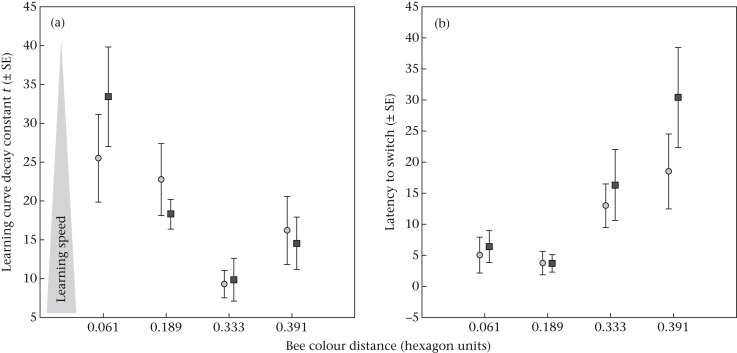
Figure 3.
(a) Mean decay constant t in the learning curve (± SE) of males (dark grey squares) and workers (light grey circles) as a function of colour distance in the hexagonal bee colour space. The t value is inversely correlated with the learning speed with high t values representing slow learning speeds and vice versa (as illustrated by the grey arrow). The colour distance of 0.061 is very small and close to the limits of discriminability (Dyer & Chittka, 2004c) whereas colour distances of >0.2 hexagon units are large and allow easy discrimination. (b) Mean number (±SE) of incorrect visits before first landing on a rewarding feeder (latency to switch) per colour distance.