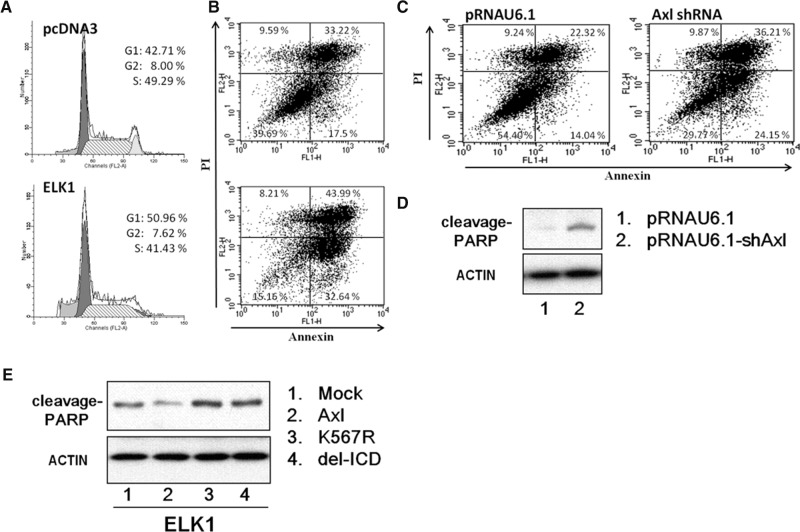
FIGURE 6.
ELK1 protein induces G1 arrest and apoptosis. (A) Cell-cycle progression of CL1-5 cells overexpressing ELK1. Cells were transfected with ELK1 or mock vector, harvested, fixed with ethanol, and stained with propidium iodide. DNA content was measured by flow cytometry. The percentage of the cell population in each of the G1, G2–M, and S phases was calculated. Representative plots of one set of triplicate experiments are shown. (B) Overexpression of ELK1 promotes apoptosis. Cells were transfected with ELK1 or mock vector for 48 h. Apoptosis was determined by annexin V-FITC/PI double staining and flow cytometry analysis. The percentage in the lower right quadrant indicates the percentage of early apoptotic cells. The percentage in the upper right quadrant indicates the percentage of late apoptotic cells. (C) Knockdown of AXL expression promotes apoptosis. CL1-5 cells were transfected with AXL shRNA or mock vector for 48 h. Apoptosis was determined by annexin V-FITC/PI double staining and flow cytometry analysis. The percentage in the lower right quadrant indicates the percentage of early apoptotic cells. The percentage in the upper right quadrant indicates the percentage of late apoptotic cells. (D) Western blot analysis of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) cleavage. Whole cell lysates were subjected to Western blotting using antibody against PARP. Actin was used as an internal control for protein loading. (E) Western blot analysis of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) cleavage. After transfection with various constructs of AXL for 24 h, cells were allowed to express ELK1 for 2 days prior to harvest. Total cell lysates were subjected to Western blot analysis for PARP protein. Actin was used as an internal control for protein loading. Mock, vector alone; AXL, full-length wild-type; K567R, kinase dead; delICD, deletion of the entire intracellular domain.