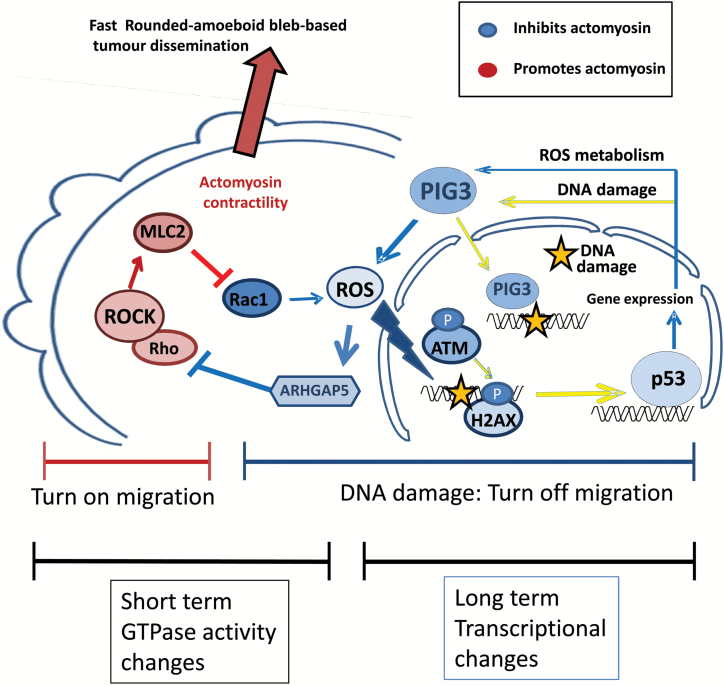
Figure 6.
Balance between Rho-ROCK and oxidative stress–induced DNA damage. Oxidative stress–dependent DNA damage results in p53 stabilization in cells with low actomyosin contractility. In turn, p53 drives the expression of several genes involved in oxidative stress metabolism and DNA damage responses, including PIG3. PIG3, apart from its DNA damage response functions, sustains production of ROS to inhibit cytoskeletal Rho-ROCK signaling through ARHGAP5, suppressing rounded-amoeboid fast tumor dissemination.