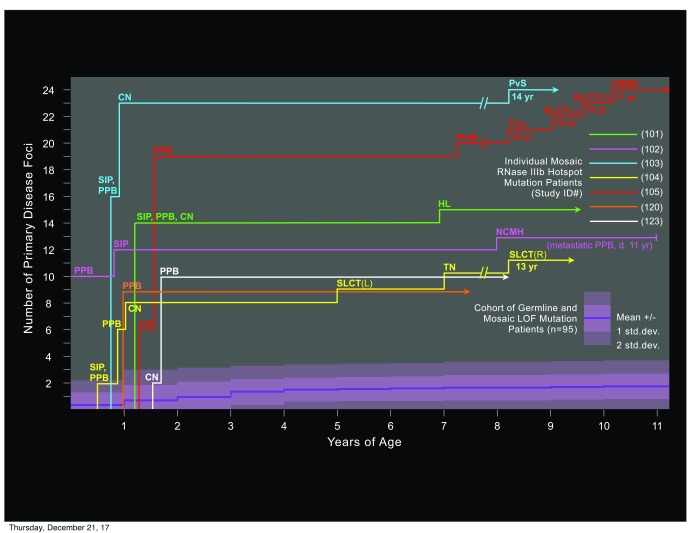
Figure 3. Numbers and types of disease foci in DICER1 syndrome patients with mosaic RNase IIIb domain hotspot mutations.
For each of the seven mosaic hotspot children identified in this study, an individual timeline indicates numbers of discrete foci of neoplastic disease and their histopathological types, graphed with respect to patient age at diagnosis. Across the lower portion of the chart, a single aggregate timeline (dark violet) represents the mean number of disease foci for all PPB/ DICER1 syndrome patients with predisposing loss of function (LOF) mutations identified in this study, graphed with respect to patient age at diagnosis. The shaded areas (in lighter violet) surrounding the timeline for LOF mutation patients indicates one and two standard deviations above and below the mean. The range of foci number among all LOF mutation patients was 0 to 6 in all years of age represented (not shown). Abbreviations: CN cystic nephroma; CBME ciliary body medulloepithelioma (eye); NCMH nasal chondromesenchymal hamartoma; PPB pleuropulmonary blastoma; PinB pineoblastoma; PvS pelvic sarcoma; SIP small intestinal polyp(s); SLCT Sertoli-Leydig cell tumor (ovary); TCa thyroid carcinoma; TN thyroid nodule(s).