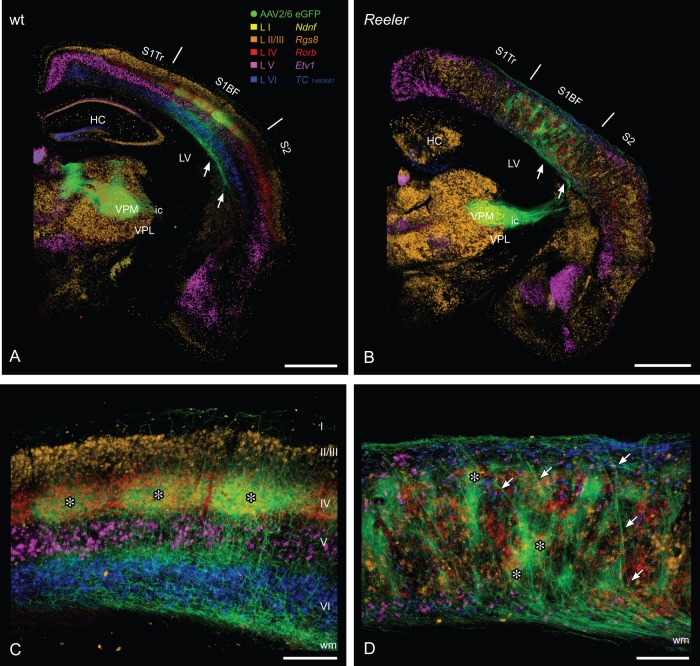
Figure 3.
Lemniscal thalamic fibers and laminar affiliation of their potential cortical target cells in the wt and reeler primary somatosensory “barrel” cortex. Combination of anterograde viral tracing (AAV2/6 eGFP) of lemniscal thalamocortical axons (TCAs) and consecutive sections with chromogenic in situ hybridization for laminar markers (A, B) GFP-labeled TCAs from the ventral posteromedial thalamic nucleus reach the wild type (A) as well as the reeler cortex (B) via internal capsule and subcortical white matter (arrows). (C) In the wild-type cortex, thalamic terminal fields predominantly are concentrated in the barrel hollows of layer IV. Thus, they show a substantial overlap with the layer IV marker (Rorb, red). To a lesser extent, thalamic terminal fields can be found at the layer V/VI boarder. The barrels and there thalamic input are marked by asterisks. (D) In the disorganized reeler cortex, TCAs first run up to the pial surface, reverse and form terminal fields at different (vertical) levels of the cortex. These patches of thalamic axons in part overlap with the layer IV marker Rorb (asterisks). Laminar markers are presented in pseudocolors, they reproduce the pattern shown in Figure 1. HC, hippocampus; ic, internal capsule; LV, lateral ventricle; S1BF, barrel field; S2, secondary somatosensory cortex; S1Tr, primary somatosensory cortex, trunk region; VPL, ventral posterolateral thalamic nucleus; VPM, ventral posteromedial thalamic nucleus; wm, white matter. Scale bars: A, B 1000 µm; C, D 250 µm.