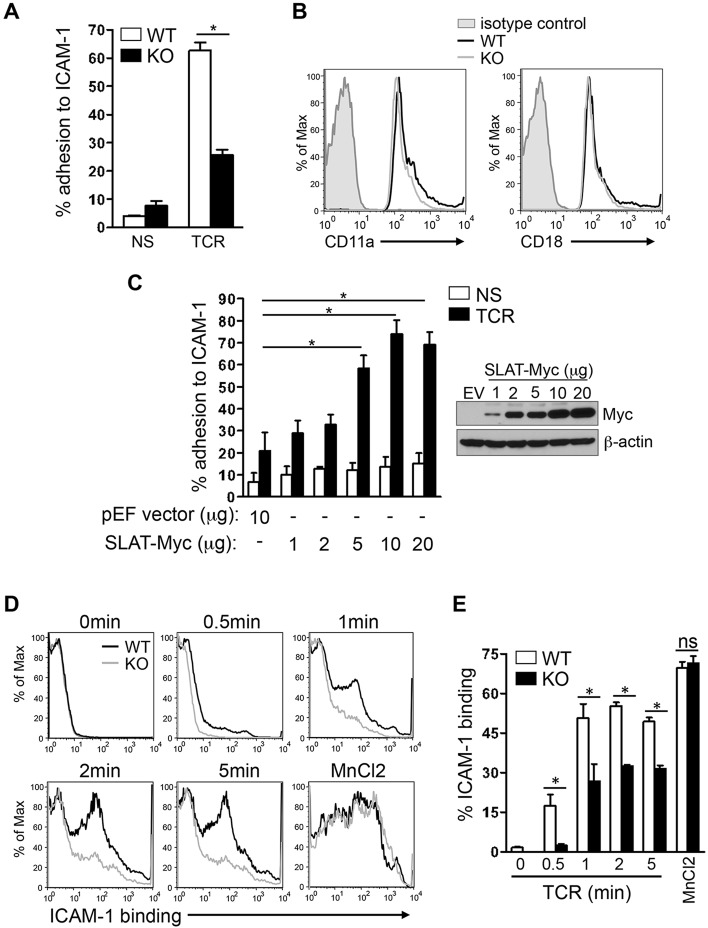
Fig. 1.
SLAT is required for TCR-induced adhesion to ICAM-1 and LFA-1 affinity maturation in CD4+ T cells. (A) Purified splenic WT and Def6−/− (KO) CD4+ T cells were left untreated (NS) or stimulated with 10 µg/ml anti-CD3 mAb (TCR) and subsequently analyzed for their ability to bind plate-bound Fc-ICAM-1 (mean±s.d., n=4). (B) WT (black line) and KO (gray line) CD4+ T cells were analyzed for the surface expression of CD11a and CD18 by flow cytometry, with normal IgG used as an isotype control (shaded). (C) Jurkat T cells transfected with 10 µg empty pEF vector (EV) or with pEF vector encoding Myc-tagged SLAT (1–20 µg) were either left unstimulated (NS) or stimulated with 10 µg/ml anti-CD3 mAb OKT3 (TCR), and subsequently analyzed for adhesion to plate-bound Fc-ICAM-1. SLAT expression was analyzed by anti-Myc immunoblotting and β-actin expression served as a loading control. Adhesion data represents the means±s.d. of four independent experiments. (D,E) WT or KO CD4+ T cells were analyzed by flow cytometry for their ability to bind soluble Fc-ICAM-1 (as a measurement of LFA-1 affinity) in response to anti-CD3 (10 µg/ml) mAb stimulation for the indicated times or 1 mM MnCl2 (positive control) treatment for 5 min. Quantitative analysis of the results shown in D, representing the mean±s.d. percentage of ICAM-1 binding (determined in triplicates) is shown in E. One out of five representative experiments is shown. *P<0.01; ns, not significant (Student's t-test).