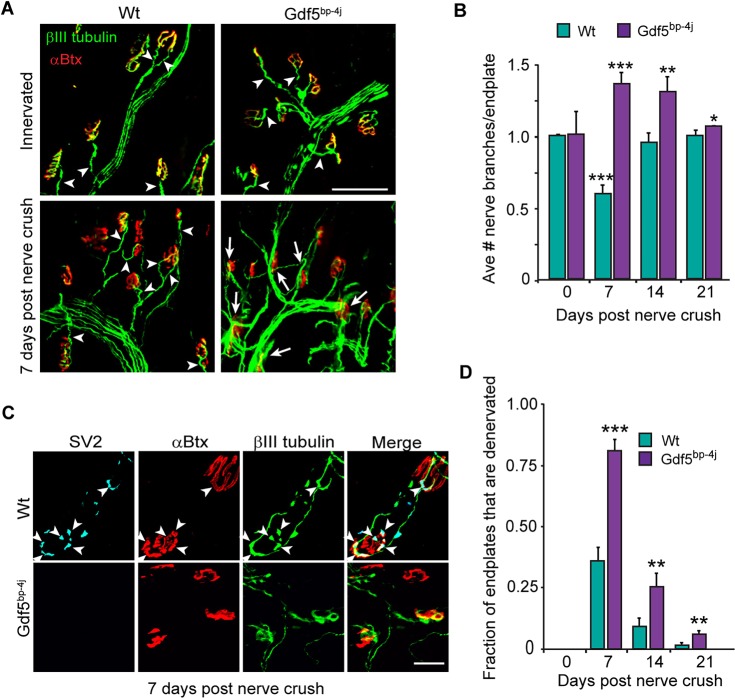
Fig. 8.
Gdf5 stimulates muscle reinnervation. (A) Representative images showing increased axonal branching over the soleus muscle in Gdf5bp-4j mice at 7 days post nerve crush. βIII tubulin+ regenerating motor nerve branches are green and αBtx+ endplates are red. Arrowheads point to a single axonal branch innervating endplates, whereas arrows point to multiple axonal branches coursing over the endplate. Scale bar: 100 µm. (B) Quantification of the number of regenerating axonal branches/endplate in Wt and Gdf5bp-4j mice. Error bars are s.d.; n=3. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001 relative to Wt. (C) Representative images showing reduced differentiation of axon terminals at endplates in Gdf5bp-4j mice at 7 days post nerve crush compared with Wt mice. SV2+ differentiated axon terminals are cyan, βIII tubulin+ regenerating motor nerves are green and αBtx+ endplates are red. Arrowheads point to SV2+ differentiated axon terminals that are also βIII tubulin+ and innervating αBtx+ endplates. (D) Quantification of denervated endplates in Wt and Gdf5bp-4j mice. Error bars are s.d.; n=3 for 7 and 14 days post nerve crush; n=4 for 21 days post nerve crush. **P<0.01; ***P<0.001 relative to Wt.