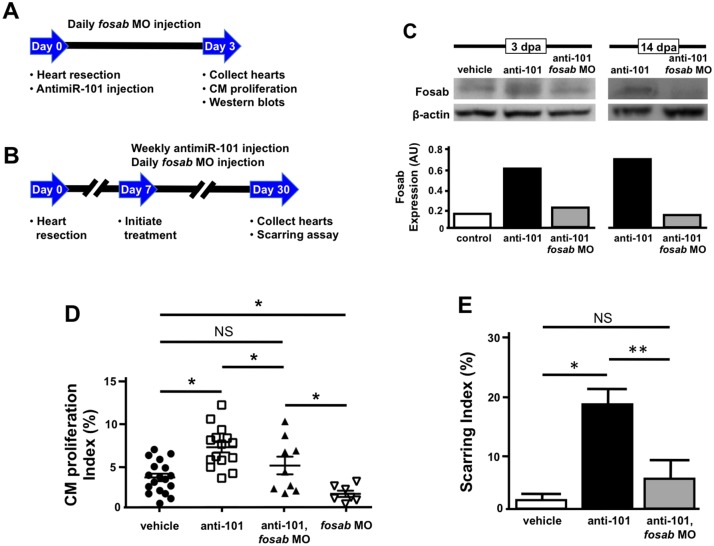
Fig. 7.
Knockdown of fosab activity rescues defects mediated by miR-101a depletion. (A,B) Experimental design for fosab vivo MO and combinatorial injections with anti-miR-101a antisense oligonucleotides. (C) Wild-type animals were injured and treated with vehicle, anti-miR-101a oligonucleotides or anti-miR-101a and fosab vivo MO for three days. Hearts were extracted and western blot hybridizations were performed to detect changes to Fosab protein. Fosab levels increase with anti-miR-101a treatment, but expression was restored to near control levels when anti-miR-101a and fosab vivo MO were co-injected. (D) Combinatorial knockdown of fosab and miR-101a activity is sufficient to rescue elevated CM proliferation indices mediated by miR-101a suppression alone. Treatment of wild-type animals with fosab vivo MO alone significantly reduced CM proliferation indices at 3 dpa compared with vehicle treatment. (E) Quantification of scar tissue was assessed at 30 dpa after vehicle, anti-miR-101a, or anti-miR-101a and fosab-vivo-MO treatment. Suppression of fosab expression between 7 and 30 dpa is sufficient to significantly decrease the scarring effect seen with suppression of miR-101a between 7 and 30 dpa. n=6-8; *P<0.05, **P<0.001 (Student's t-test); NS, not significant; error bars represent s.e.m.