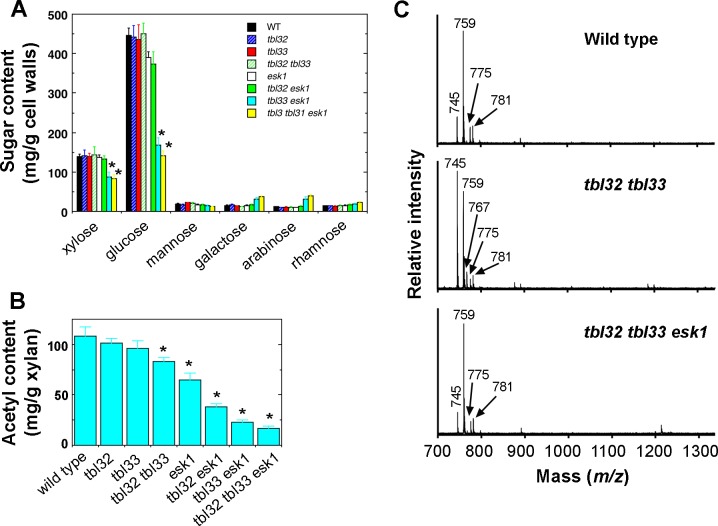
Fig 7. Measurement of cell wall sugar composition and acetyl contents in the wild type and various mutants.
The inflorescence stems of 8-week-old wild type and esk1 plants, 12-week-old tbl33 esk1 plants, and 16-week-old tbl32 tbl33 esk1 plants were used for extraction of cell wall residues and xylan. (A) Cell wall composition analysis revealed a reduction in the amounts of xylose and glucose in tbl33 esk1 and tbl32 tbl33 esk1 compared with the wild type and esk1. (B) Acetyl contents in DMSO-extracted xylans of the wild type and various mutants. Note the drastic reduction in the acetyl contents in tbl32 esk1, tbl33 esk1, and tbl32 tbl33 esk1. Error bars denote SD of the data from three separate pools of samples. Asterisks in (A) and (B) indicate statistically significant differences compared with the wild type (p < 0.001). (C) MALDI-TOF-MS analysis of xylooligomers generated by endoxylanase digestion of KOH-extracted xylan from the wild type (top panel), tbl32 tbl33 (middle panel) and tbl32 tbl33 esk1 (bottom panel). The ion peaks at m/z 745 and 759 are attributed to (GlcA)Xyl4 and (MeGlcA)Xyl4, respectively. Those at m/z 767 and 781 correspond to the disodiated species of (GlcA)Xyl4 and (MeGlcA)Xyl4, respectively. The ion at m/z 775 corresponds to (Gal-GlcA)Xyl3 [38].