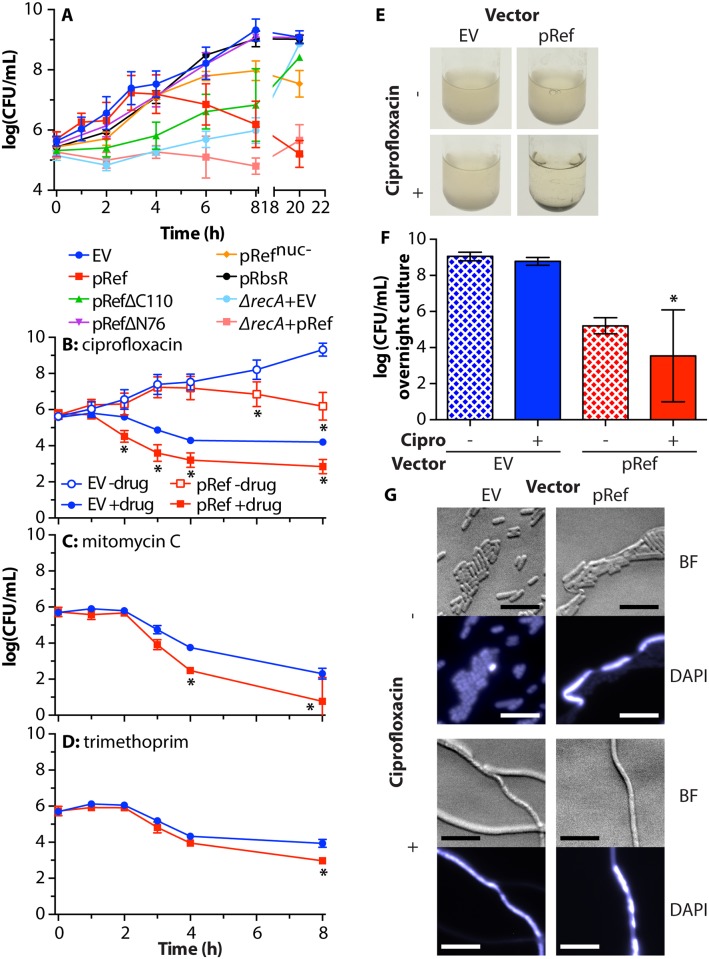
Fig 6. Ref is toxic to E. coli in stationary phase and enhances lethal effects of DNA-damaging antibiotics.
A. Cell survival during Ref and variant expression. WT E. coli strains EAR61 (EV), EAR62 (pRef), EAR73 (pRefΔC110), EAR98 (pRefΔN76), EAR105 (pRefnuc-), EAR104 (pRbsR), and ΔrecA strains EAR64 (EV) and EAR65 (pRef) were grown to log-phase, adjusted to 5x105 CFU/mL, treated with 1% arabinose, and outgrown for one day at 30°C. Cells were plated and the average and standard deviation of CFU/mL for at least three biological replicates for each condition are reported. Significant p-values can be found in S1 Table. B. WT E. coli strains EAR61 (EV) and EAR62 (pRef) were grown as described in (A), but with the addition of water or 8 ng/mL ciprofloxacin in addition to 1% arabinose. Cells were plated and data was reported as in (A). * = p-value<0.001, when compared to EV with same treatment. C. Same as (B) except 5 μg/mL mitomycin C was used instead of ciprofloxacin. * = p-value<0.001, when compared to EV with same treatment. D. Same as (B) except 0.5 μg/mL trimethoprim was used instead of ciprofloxacin. * = p-value<0.001, when compared to EV with same treatment. E. Images of cultures from (B) after overnight incubation. F. Quantification of viable cells in panel (E). Average and standard deviation of 4–8 biological replicate cultures are reported. * = p-value<0.001, when compared to EV with same treatment. G. Microscopy of cells in panel (E), obtained as in Fig 4C. Scale bar = 10 μm.