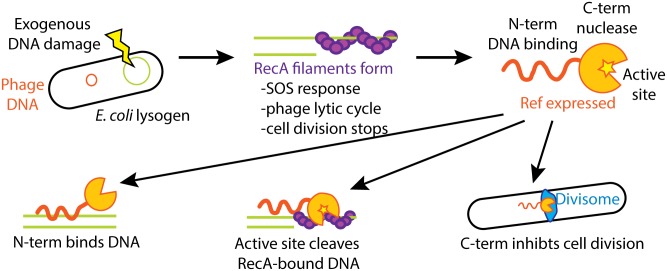
Fig 8. Multiple roles for Ref protein during the P1 lytic cycle.
When a P1 lysogen is exposed to a DNA damaging agent (such as cipro), RecA filaments form near the damaged DNA sites. This causes (1) E. coli SOS response induction, (2) induction of phage lytic cycle, (3) inhibition of cell division. Ref protein is produced during the phage lytic cycle and performs three functions: (1) the Ref N-terminal DNA binding domain binds bacterial DNA, inhibiting other DNA metabolism enzymes, (2) the nuclease active site of Ref cleaves RecA-bound DNA to enhance the bacterial SOS response, (3) Ref inhibits cell division mainly via its C-terminal domain, and possibly through an interaction with the bacterial divisome.