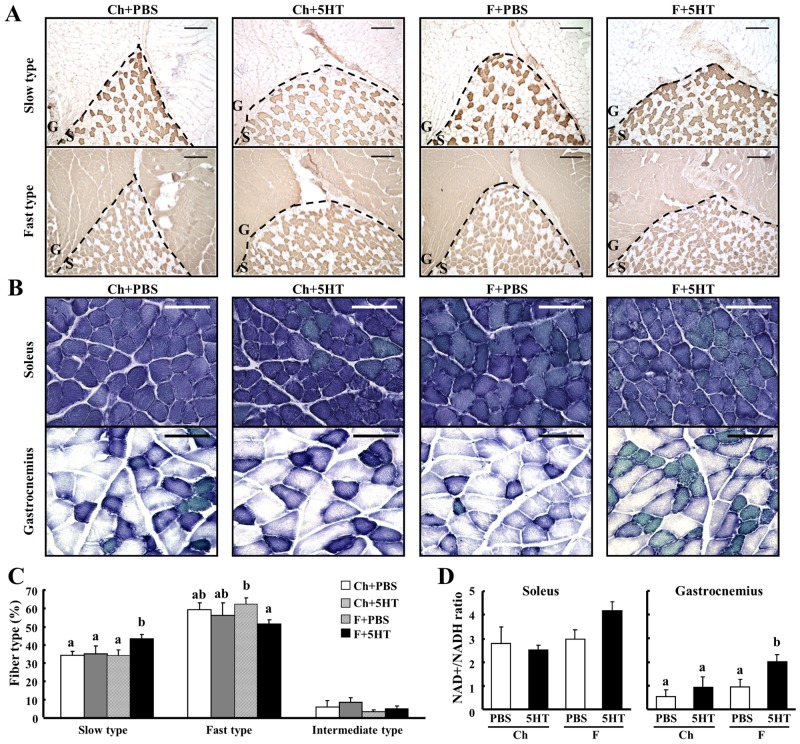
Fig 4. 5-HT elevates the proportion of slow type muscle fibers in the skeletal muscle of mice on the high fat diet.
A, Mice fed a chow diet (Ch) or a high fat diet (F) were i.p. injected with PBS or 5-HT (1 mg/mouse) twice a week. After 8 weeks of treatment, the frozen sections of soleus and gastrocnemius muscles of 14 weeks of age mice were immunostained using anti-slow and anti-fast myosin heavy chain antibodies, specific markers of myofiber type-I and type-II, respectively (n = 5). S and G in (A) indicate the positions of soleus and gastrocnemius muscles, respectively. Bars in histological sections indicate 200 μm. B, The activities of oxidative enzyme in soleus and gastrocnemius muscles of mice at 14 weeks of age of each group were examined by enzymatic staining using NADH-tetrazolium reductase (NADH-TR) shown with a blue precipitate. Bars in histological sections indicate 50 μm. C, The proportions of slow, fast and intermediate type muscle fibers in soleus muscle of each group of mice were calculated by evaluating the type of all soleus muscle fiber in each immunostaining section in (A) (n = 5). D, Intracellular levels of NAD-to-NADH ratio were measured in soleus and gastrocnemius muscles of mice at 14 weeks of age (n = 5–7). Data are the mean ± s.e. Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA. Columns with a different letter are significantly different (p<0.05).