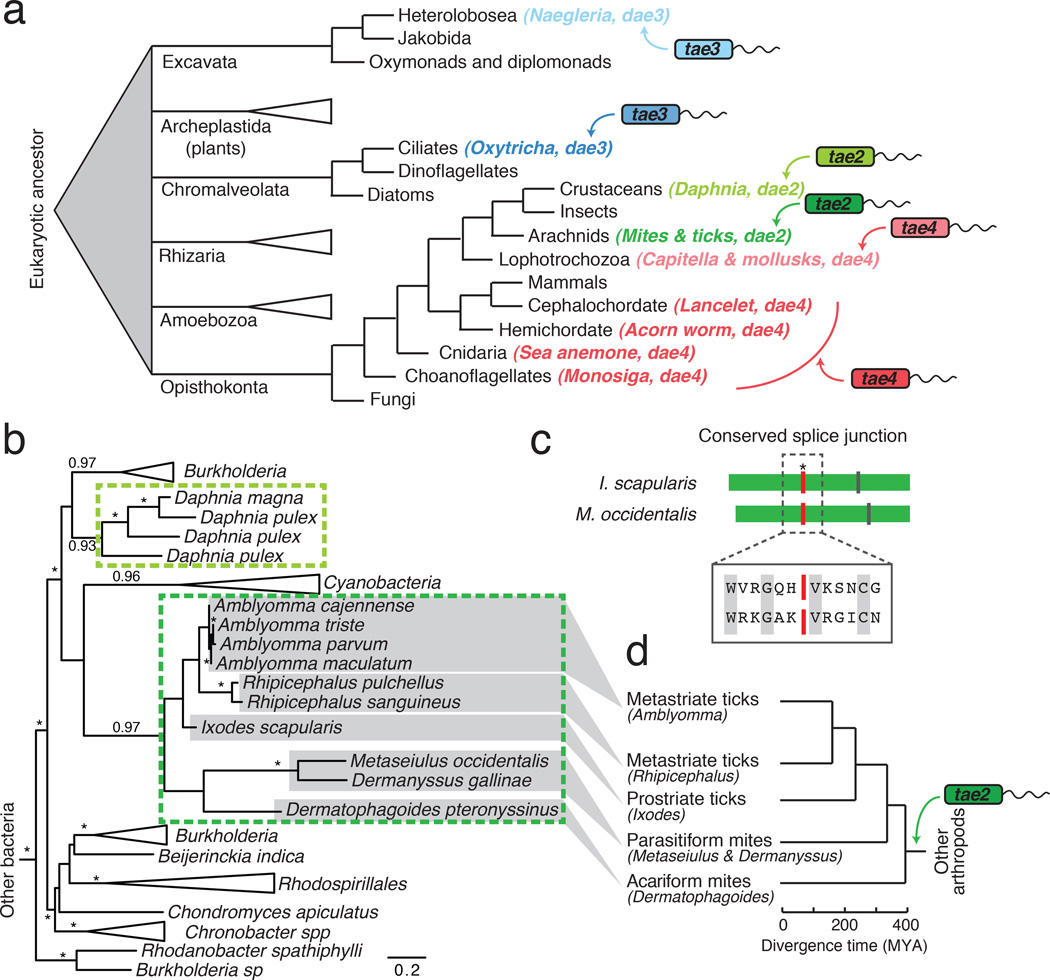
Figure 1. Recurrent horizontal gene transfer of type VI amidase effector (tae) genes into diverse eukaryotic lineages.
a, Schematized phylogenetic tree of basal eukaryotic lineages28 showing instances of tae transfer (arrows) from bacteria to eukaryotes, coded by color (tae family) and shading (acquisition events). b, Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree of tae2 and dae2 genes. Representatives are boxed and color-coded according to Fig. 1a. Branch support > 0.7 indicated by asterisks or numbers. Scale bar shows estimated divergence in amino acid changes per residue. Dashed lines highlight separate HGT events. c, Schematic alignment of tick (I. scapularis) and mite (M. occidentalis) dae2 genes with shared (red line, asterisk) and unique (vertical lines) intron positions denoted. Aligned residues surrounding the splice site are shown (boxed) with conserved amino acids indicated (grey). d, Tick and mite phylogeny with approximate dates of divergence based on concordance with the dae2 gene tree (c)14.