Fig 5. F-actin polarization is dependent on the vulval precursor cells and CDC-42.
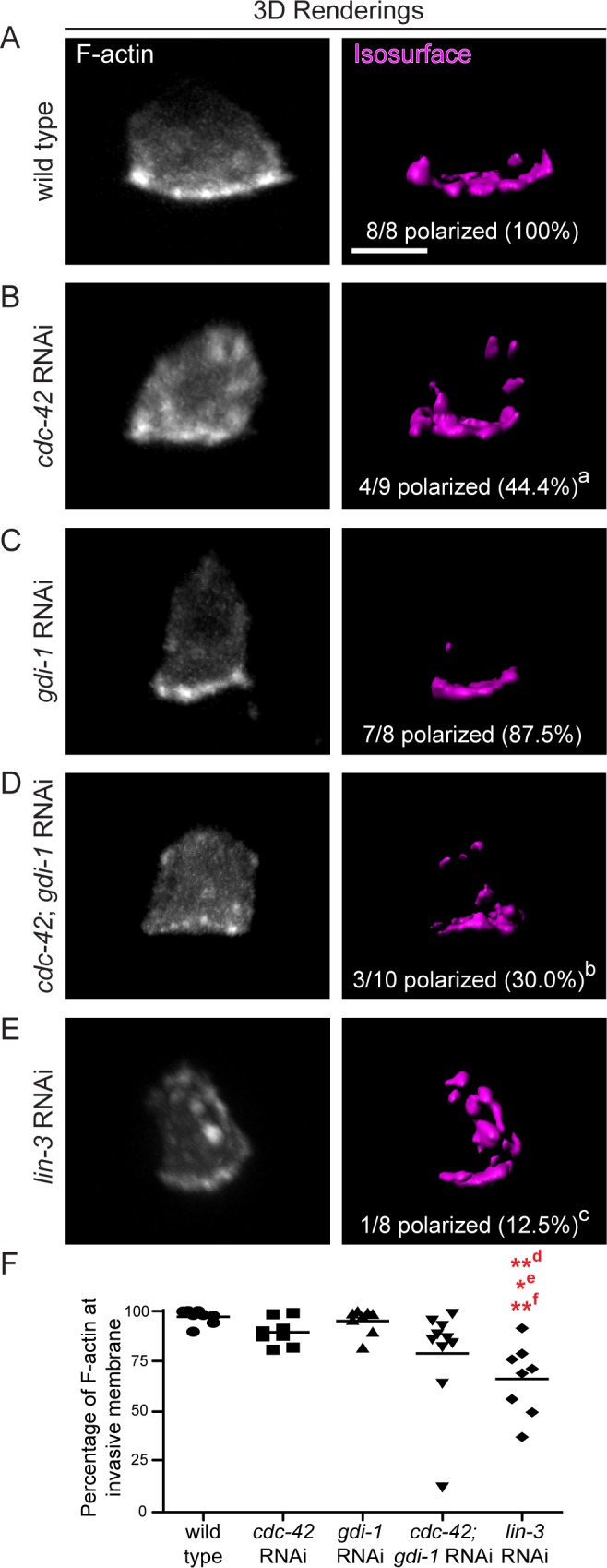
(A-E) 3D projections (left) and isosurface renderings of a fluorescent F-actin probe (cdh3>mCherry::moeABD) in wild type animals (A), animals treated with RNAi against cdc-42 (B), RNAi agianst gdi-1 (C), double RNAi targeting cdc-42 and gdi-1 (D, cdc-42; gdi-1 RNAi), and animals lacking the vulval precursor cells (E, lin-3 RNAi). F-actin was mispolarized after targeting cdc-42 (a p < 0.05), cdc-42 and gdi-1 in combination (b, p = 0.004), and the vulval precursor cells (lin-3 RNAi; c p = 0.001). Comparisons were made using Fisher’s exact tests. (F) Scatter plot showing the percentage of F-actin polarized to the invasive membrane (line shows mean). The most severe of F-actin mispolarization defect was observed after loss of the vulval precursor cells (lin-3 RNAi; n > 8 animals per group; **d p < 0.01 vs. wild type, *e p < 0.05 vs. cdc-42 RNAi, **f p < 0.01 vs. gdi-1 RNAi). Comparisons were made using a Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. Scale bars = 5 μm.
