Fig. 3.
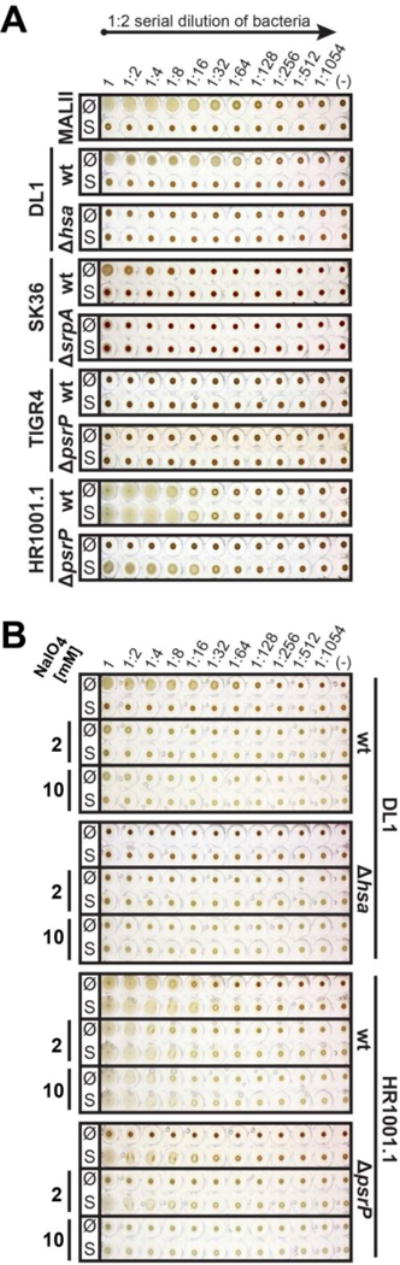
Streptococcal-mediated hemagglutination of human red blood cells. Two-fold serial dilutions of S. gordonii DL1, S. sanguinis SK36, S. pneumoniae wild-type strain TIGR4, capsule-free mutant strain HR1001.1, and respective isogenic SRR adhesin-deficient mutants were mixed and incubated with human red blood cells. The sialic acid specific lectin from Maackia amurensis (MAL II) was used as a control for the presence or loss of sialic acid residues. A, Hemagglutination done with untreated (Ø) or sialidase-treated (S) RBCs. B, Treatment of RBCs with 2 mM or 10 mM sodium periodate to oxidize sialic acids or general glycans, respectively, prior to hemagglutination.
