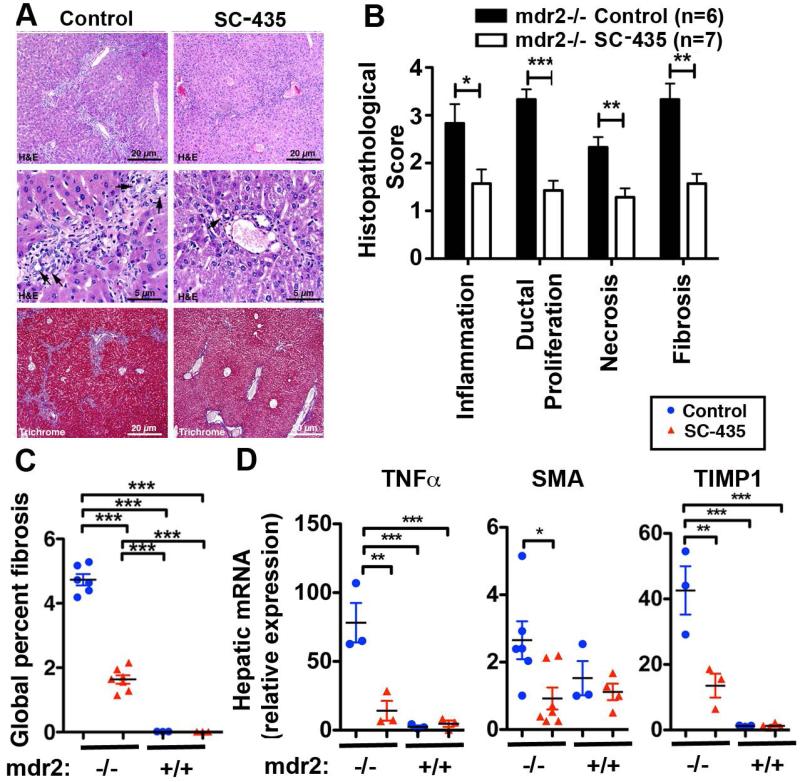
Figure 3. SC-435 treatment is associated with reduced periportal inflammation and fibrosis in mdr2−/− mice.
Sections from paraffin embedded liver samples obtained from mdr2−/− mice on DOT 14 were subjected to H&E and Trichrome staining. Representative photomicrographs of sections are shown in A, with arrowheads denoting bile duct profiles. The components of sclerosing cholangitis score (inflammation, ductal proliferation, necrosis, and fibrosis) were analyzed on a 1 to 4+ scale (B). Trichrome stained slides from livers of SC-435-treated and control mdr2−/− mice were subjected to automated Aperio-based tissue image analysis to quantify the percentage of liver fibrosis (C). Total hepatic RNA from 44-day old mice of the four groups was subjected to qPCR and relative expression of the pro-inflammatory gene TNFα and of the profibrogenic genes SMA and TIMP1 was computed by ΔΔCT analysis using HPRT as the house keeping gene (D). Statistical analysis: unpaired t test was applied to the data of the two groups (SC-435 vs control) in mdr2−/− mice in B, with *, **, *** denoting p-values of <0.05, <0.01, <0.001, respectively, and one-way ANOVA in C and D.