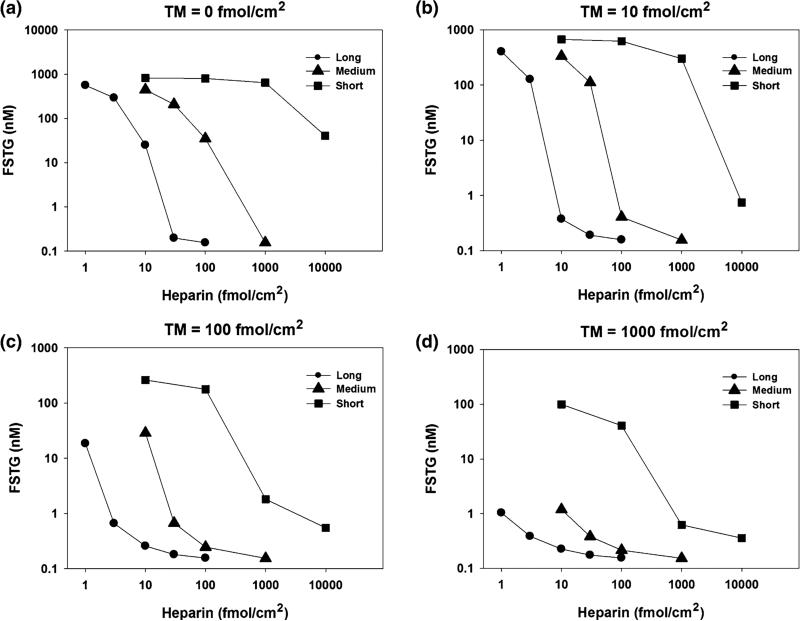
FIGURE 5.
The effect of distinct surface bound heparin species and thrombomodulin under venous shear conditions. FSTG was measured in response to varying TM and heparin surface densities, with surface bound tissue factor density set just above the cutoff level to 1.4 fmol/cm2 and at a shear rate 50 s−1. Three different heparin chain lengths were used: short (5 saccharides), medium (26 saccharides), and long (70 saccharides). While high levels of surface bound TM and heparin alone inhibit thrombin generation, these results suggest that a combination of moderate levels of TM and heparin work in concert to inhibit the coagulation cascade. For instance, thrombin formation is fully inhibited (FSTG < 10 nM) at a TM surface density of 100 fmol/cm2 and at a surface density of long chain heparin of 3 fmol/cm2. Surface bound TM or heparin alone would require tenfold higher levels to achieve similar levels of inhibition. Additionally, long chain heparin was significantly more effective at inhibiting thrombin generation as compared to short chain heparin.