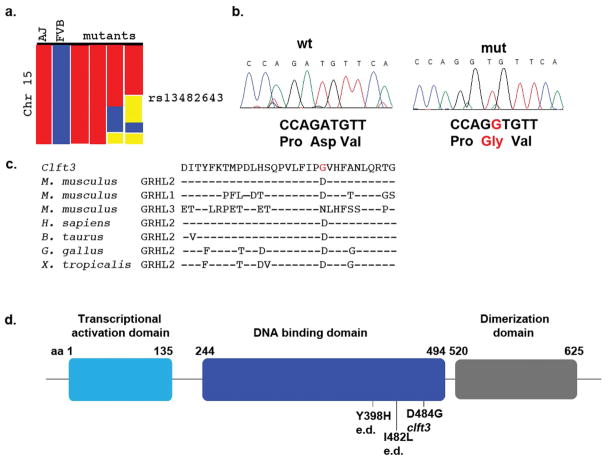
Figure 3. Cloning of the clft3 mutation.
(A) A whole-genome SNP scan originally identified a region on chromosome 15 containing the clft3 mutation from the proximal end to SNP rs13482643 (red = homozygous for A/J SNP, blue = homozygous for FVB/NJ SNP, yellow = heterozygous). (B) Sanger sequencing of the Grhl2 locus identified an A>G missense mutation in clft3 mutants. (C) The ENU-induced mutation changes the coding of a well-conserved amino acid from aspartic acid to glycine (red text). Amino acid sequence from all three mouse Grhl proteins and Grhl2 sequence from four other vertebrates are indicated (- indicates same residue as above sequence). (D) A graphical representation of the protein domains of Grhl2 shows the clft3 mutation is in the DNA binding domain (blue) of the Grhl2 protein. The location of point mutations in human ectodermal dysplasia patients (e.d.) are also indicated.