Figure 1. Acute resistance exercise on muscle protein synthesis .
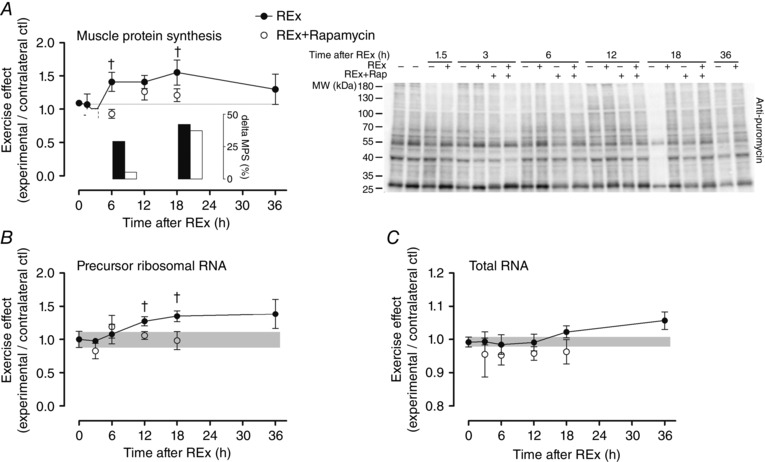
The effect of acute resistance exercise (REx, closed circles) on muscle protein synthesis (MPS; A; P = 0.042, for effect of time; representative blot at right), precursor ribosomal RNA (B; P = 0.054, for effect of time) and total RNA (C; P = 0.085, for effect of time). The ‘0’ time point is a non‐stimulated control group with its error term shaded to aid visual comparisons. Rapamycin was administered (pre‐exercise, 1.5 mg kg−1 by i.p. injection) to groups shown in open circles. MPS was assessed by measuring the incorporation of puromycin into nascent peptides by Western blot; inset shows change in MPS from the initial time point of each group to MPS at 6 and 18 h. Newly synthesized pre‐rRNA was measured using internal transcribed spacer 1 gene expression as a readout. †Difference between REx and REx+Rapamycin at the same time point, P < 0.05. Values are expressed as experimental/contralateral control muscles, means ± SEM.
