Figure 1. Hypoxia increased ROS in uterine arteries .
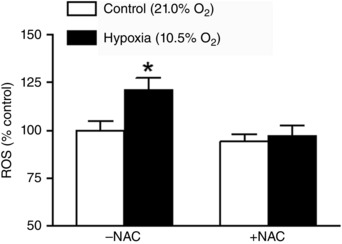
Uterine arteries of pregnant sheep were treated under control (21.0% O2) and hypoxia (10.5% O2) for 48 h in the absence or presence of 1 mm N‐acetylcysteine (NAC). ROS were measured with a DCF‐based quantitative assay kit. Data are means ± SEM of four tissues from four animals of each group. Data were analysed with two‐way ANOVA. *P < 0.05, hypoxia vs. control.
