Figure 3. N‐Acetylcysteine ablated hypoxia‐mediated decrease in NS1619‐induced relaxations in uterine arteries .
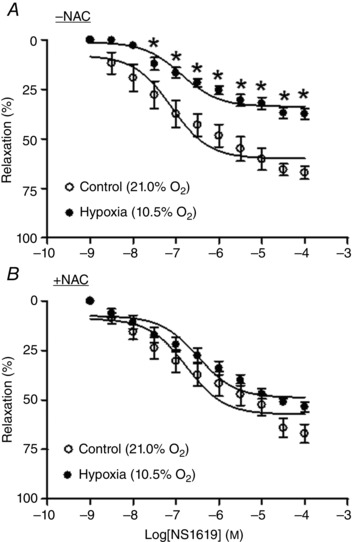
Uterine arteries of pregnant sheep were treated under control (21.0% O2) and hypoxia (10.5% O2) for 48 h in the absence or presence of 1 mm N‐acetylcysteine (NAC). NS1619‐induced relaxations were determined after the treatments. Data are means ± SEM of five tissues from five animals of each group. Data were analysed with repeated measures ANOVA. *P < 0.05, hypoxia vs. control.
