Fig 3. Dendritic length of Golgi Cox-impregnated layer V pyramidal neurons in the peri-infarct cortex and in the corresponding contralateral cortex.
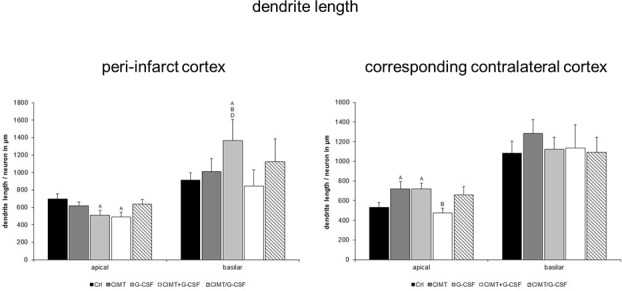
Quantitative analysis yielded a decrease in the mean length of the apical dendrites and an increase of the basilar dendrites in the peri-infarct cortex of the G-CSF group which was associated with significantly improved functional outcome in this group as recently shown [6]. However, the combined G-CSF and CIMT groups with a similar degree of functional recovery [6] lacked respective changes in the basilar dendritic length. In the corresponding contralateral cortex, a significant increase of the mean dendritic length of the apical dendrites of both G-CSF and CIMT treated rats without alterations of the basilar dendrites was seen (A, B, D, significant difference compared with control, CIMT, CIMT+G-CSF, respectively; values are expressed as length/neuron in μm ± SEM; p<0.05).
