Figure 2.
Combination of the ATR Inhibitor VE-821 and the CHK1 Inhibitor AZD7762 Synergistically Kills Cancer Cells
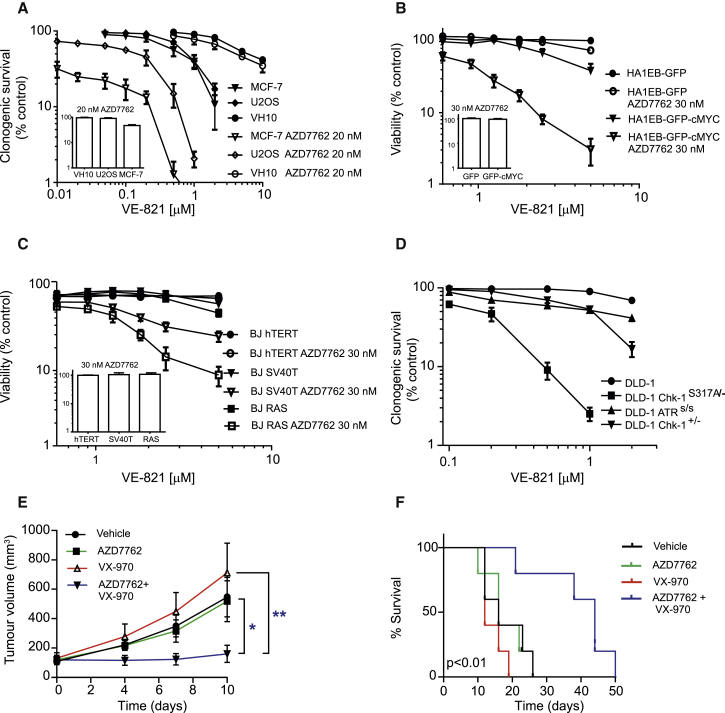
(A) Clonogenic survival of U2OS, VH-10, and MCF-7 cells. The 500 (U2OS and MCF-7) or 1,000 (VH-10) cells were seeded in 10-cm2 dishes, and, after 5-hr incubation, the inhibitors were added directly to the media. After 72-hr incubation, drug-containing media were replaced with fresh media and cells were kept for another 5–8 days before colonies were stained with methylene blue. Quantitative data: n = 3, mean ± SEM.
(B) Parental and cMYC-transformed cells were treated with the indicated doses for 72 hr. At the end of the incubation period, resazurin was added and cell viability was measured. Quantitative data: n = 3, mean ± SEM.
(C) BJ-hTERT, BJ-hTERT SV40, and BJ SV40 RAS cells were treated with the indicated doses for 72 hr. At the end of the incubation period, resazurin was added and cell viability was measured. Quantitative data: n = 3, mean ± SEM.
(D) CHK1 functionally compromised cells are sensitive to ATR inhibitor. Clonogenic survival of DLD-1, DLD-1 CHK1S317A/−, DLD-1 CHK1+/−, and DLD-1 ATRS/S after ATR inhibitor VE-821 treatment is shown. A similar protocol was used as for U2OS and VH-10 cells. Quantitative data: n = 3, mean ± SEM.
(E) Therapeutic efficacy of combined inhibition of ATR and CHK1 in mouse tumor models. Therapeutic efficacy of VX-970 and AZD7762 in H460 lung cancer xenografted mice is shown. BALB/c nude mice bearing H460 xenograft were divided in four groups (five animals in each group) with a tumor volume of ∼130 mm3 in each group. The first control group of animals was treated with vehicle (orally and intraperitoneally). The second group of animals was treated with 25 mg/kg body weight of CHK1 inhibitor AZD7762 (intraperitoneal route). The third group of animals was treated with 60 mg/kg body weight of ATR inhibitor VE-822 (oral administration), and the fourth group received a combination of both CHK1 and ATR inhibitors. Vehicle and drugs were administered on days 0–3, 10–12, and 18–20 irrespective of no mice survival in each group. Tumor volume was measured with calipers and is shown here as mean ± SEM. Statistical significance was determined using two-way ANOVA with repeated measurement (∗p < 0.05 and ∗∗p < 0.01).
(F) Kaplan-Meier survival curve of H460-xenografted mice. When tumor size reached 1,000 mm3, the animal was sacrificed.