FIGURE 1.
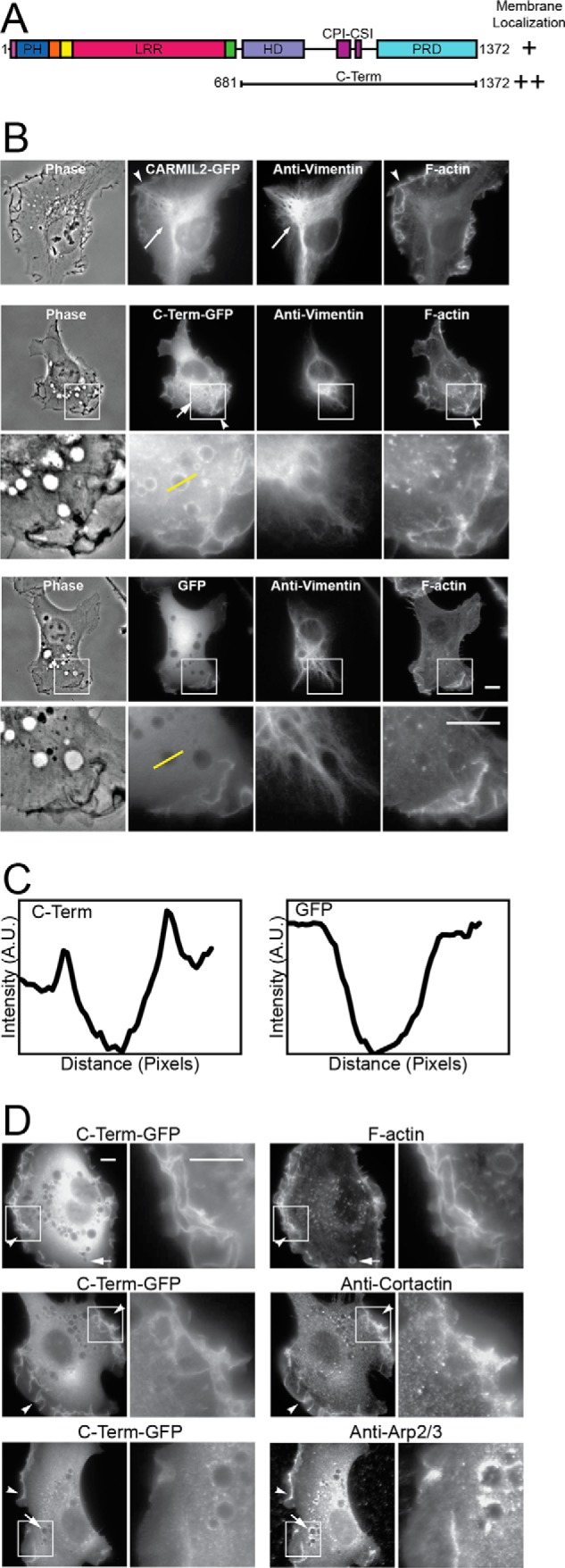
C-terminal half of CARMIL2 localizes to membranes. A, domain architecture of CARMIL2, indicating the CARMIL2 C-terminal portion (C-Term) used here. B, localization of full-length CARMIL2 (upper panels) and C-term (middle panels), as GFP fusions, compared with vimentin and F-actin, in HT1080 cells. Plain GFP (lower panels) is a negative control. Boxed regions are shown at higher magnification. Long arrows, co-localization of CARMIL2 with vimentin. Short arrows, puncta of CARMIL2 C-Term-GFP on macropinosomes. Arrowheads, ruffling membranes at the leading edge. Yellow lines indicate location of the line scans for panel C. Scale bars, 10 μm. C, line scans through macropinosomes in images from panel B. CARMIL2 C-Term-GFP fluorescence intensity shows peaks at the edges of macropinosomes. GFP, a negative control, does not. D, dual localization of CARMIL2 C-Term-GFP with F-actin and actin regulators. F-actin and Arp2/3 complex co-localize with CARMIL2 C-Term at leading-edge membranes and macropinosomes. Cortactin co-localizes at leading-edge membranes, but not macropinosomes. Boxed regions are shown at higher magnification. Scale bars, 10 μm.
