FIGURE 10.
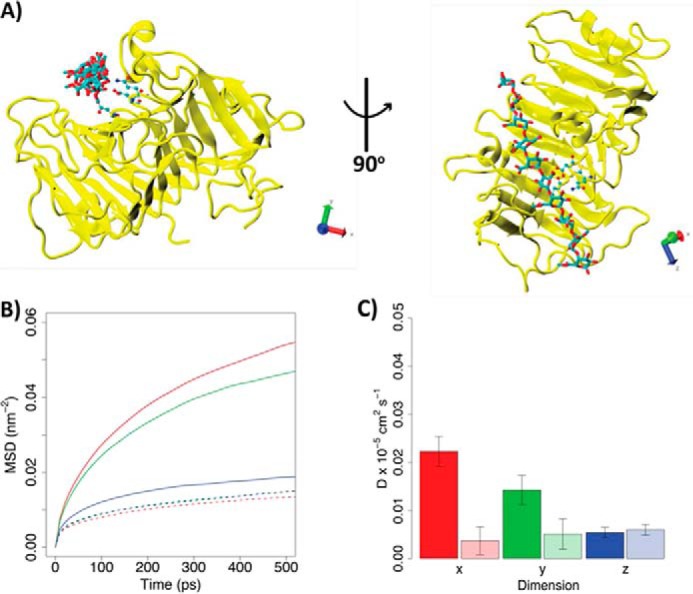
Diffusion of HG decasaccharide (X5XM4) docked into the binding grooves of processive Ani-PME2 and processive Ech-PME. A, structure of Ani-PME2 in complex with the X5XM4 decasaccharide modeled into the enzyme binding groove. Ani-PME2 is colored in yellow, and the oligosaccharide is shown in licorice and colored by atom type. The binding of X5XM4 to Ech-PME is generally similar and is shown in Ref. 74. The Cartesian axes show the alignment of the oligosaccharide along the z-dimension. B, mean-square displacements of the oligosaccharide during the first 500 ps from the start of the simulation in the x (red), y (green), and z (blue) dimensions. The solid line refers to Ani-PME2; the dotted line shows Ech-PME. The mean-square displacement in the z direction is very similar for both enzymes. C, diffusion coefficients calculated from the fitting of the mean-square displacements shown in B between 100 and 400 ps. Diffusion coefficients describe the movements of the oligosaccharide along the x (red), y (green), and z (blue) dimensions. The z-direction represents the direction of oligosaccharide sliding in the case of a processive activity. The fully colored boxes refer to Ani-PME2; the pale-shaded boxes show Ech-PME. The diffusion of the oligosaccharide is markedly greater in the x-direction, away from the substrate-binding groove, for the non-processive Ani-PME2 than for the processive Ech-PME.
