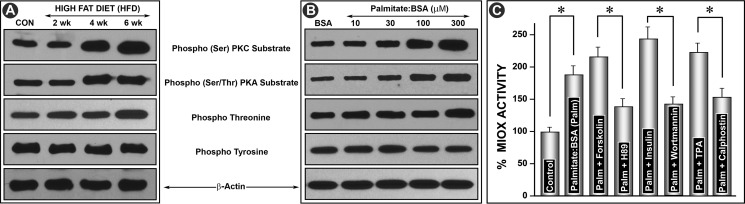
FIGURE 2.
Modulation of phosphorylation of Miox and its activity by HFD and albumin-bound fatty acids. Kidney homogenates or cellular lysates were immunoprecipitated with substrate-specific phosphoantibodies to PKA (Ser/Thr) and PKC (Ser) and to phosphothreonine and phosphotyrosine residues followed by Western blot analyses with anti-Miox antibody. A time-dependent (2–6 weeks) increased phosphorylation was observed with phosphoantibodies directed against serine and threonine residues (A). Similarly, a dose-dependent increase in the phosphorylation at serine and threonine residues was observed in cells treated with various concentrations of palmitate/BSA (B). No increase was observed in samples immunoprecipitated with anti-phosphotyrosine antibody. Concomitant treatment with palmitate/BSA and activators of PKA (forskolin), PDK/PI3K (insulin), and PKC (TPA) further increased the Miox activity (C). Concomitant treatment with respective inhibitors, i.e. H89 (PKA), wortmannin (PI3K), and calphostin (PKC), reduced the activity below the levels induced by palmitate/BSA alone, confirming that fatty acid-induced activity is phosphorylation-dependent (C). *, p < 0.01 versus control or inhibitor versus activator n = 4.