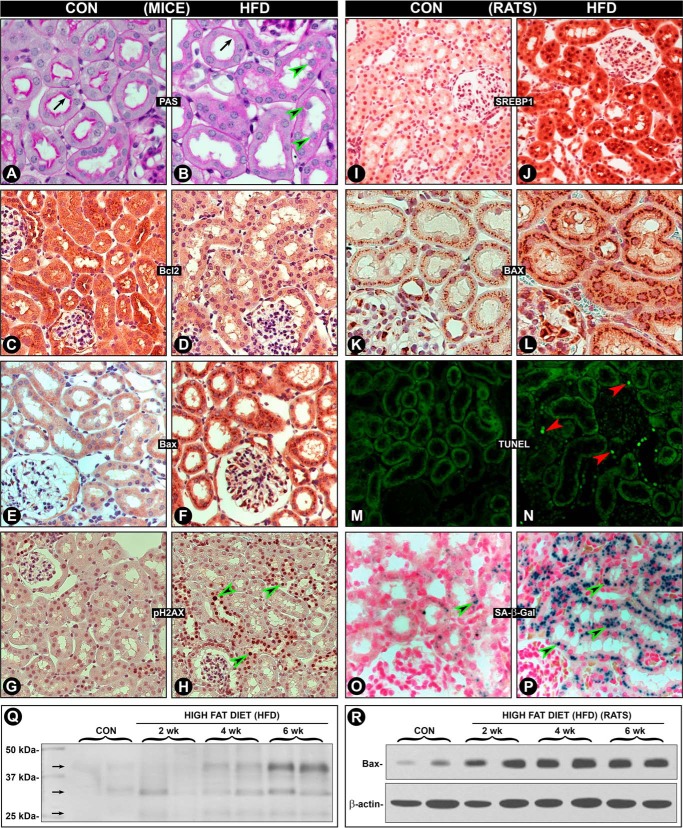
FIGURE 5.
Modulation of Srebp1 expression, cytoplasmic and nuclear alterations, senescence, apoptosis, and urinary protein excretion in mice and rats by HFD. Studies were performed to assess the effect of HFD on morphologic and biochemical changes in both the species in metabolically active tubular compartment. In mice, a loss of the pink staining luminal brush border (A versus B, arrows) with extrusion of nuclei of tubular cells was observed (arrowheads). The Bcl2 expression was decreased, and that of apoptogenic Bax was increased (C–F). Anti-pH2AX-associated nuclear staining (reflective of nuclear DNA damage) was seen in many tubular nuclei of mice fed an HFD (G versus H, arrowheads). Tubular damage was also reflected in increased time-dependent urinary excretion of low molecular proteins ranging from 30 to 45 kDa (Q, arrows). Some of the changes seen in kidney tubules of rats fed with HFD are depicted here. Identical to the Miox expression, an increased expression of Srebp1 (I versus J) and BAX (K versus L) was observed. The increased expression of Bax was time dependent (R). This was associated with increased apoptosis, as highlighted by TUNEL staining (M versus N). In addition, a marked increase in SA-β-Gal staining was observed (O versus P, arrowheads), suggesting an increased replicative capacity of tubular cells following HFD-induced cellular damage. Overall, these changes suggest that HFD adversely affect the cellular homeostasis in both the species.