Fig. 4.
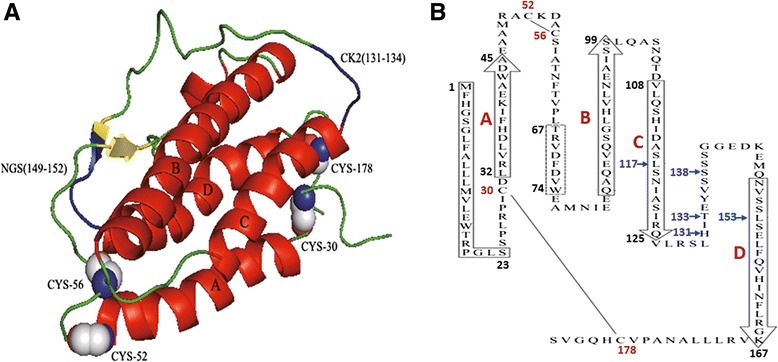
The three-dimensional structure of the G. dobula EPO. a Ribbon diagram of the predicted G. dobula EPO tertiary structure. The four α-helices are labeled A–D (red). Disulfide bonds bridge the residues 30–178 and 52–56. The important functional sites (NGS and CK2) are marked in blue. This folding pattern is strongly suggested by the large size of the two interconnecting loops AB and CD. b Schematic representation of the G. dobula EPO primary structure depicting the predicted up–up–down–down orientation of the four antiparallel α-helices (boxes with arrowheads). An apparent signal peptide sequence of 23 amino acids is delineated by the solid rectangle. The limits of each helix were drawn according to the human EPO protein sequence, as in Fig. 2. The dashed rectangle shows a predicted short region of the β-sheet. The locations of the two disulfide bridges are shown. Amino acid sites under positive selection (117 L, 131H, 133 T, 138S, and 153 L) are represented by blue arrows
