Figure 2. Redundant function of SERK family RLKs in stomatal patterning.
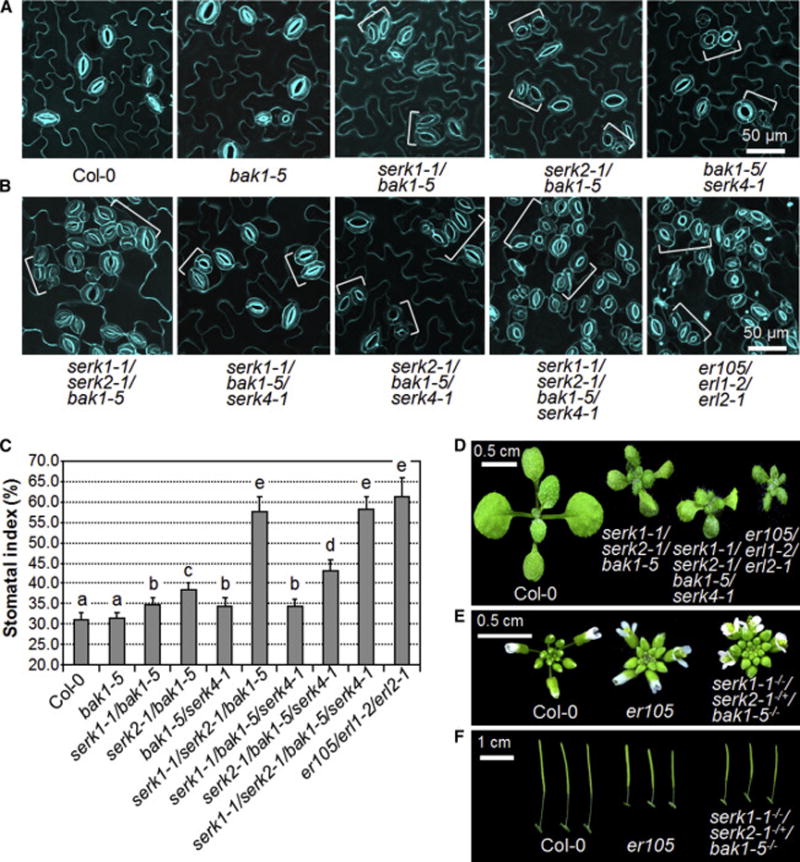
(A–C) The serk1-1/serk2-1/bak1-4 mutant but not other serk mutants shows stomatal patterning defects. Confocal images of indicated genotypes were taken on the abaxial cotyledon epidermis of 10-day-old seedlings grown on ½ MS plates. The representative images were selected from at least five replicates. Brackets indicate clustered stomata (C). (D) The seedling phenotypes of two-week-old serk1-1/serk2-1/bak1-4 and er105/erl1-2/erl2-1 mutants grown on soil. (E) Abaxial cotyledon stomatal index of 10-day-old seedlings, expressed as percentage of the number of stomata to the total number of epidermal cells. The data are shown as mean + SD (n=8). Asterisks above the columns indicate significant difference compared with the data from WT plants (*** P<0.0001, Student’s t-test). The experiments were repeated three times with similar results. (see also Figures S2 and S3).
