Figure 4.
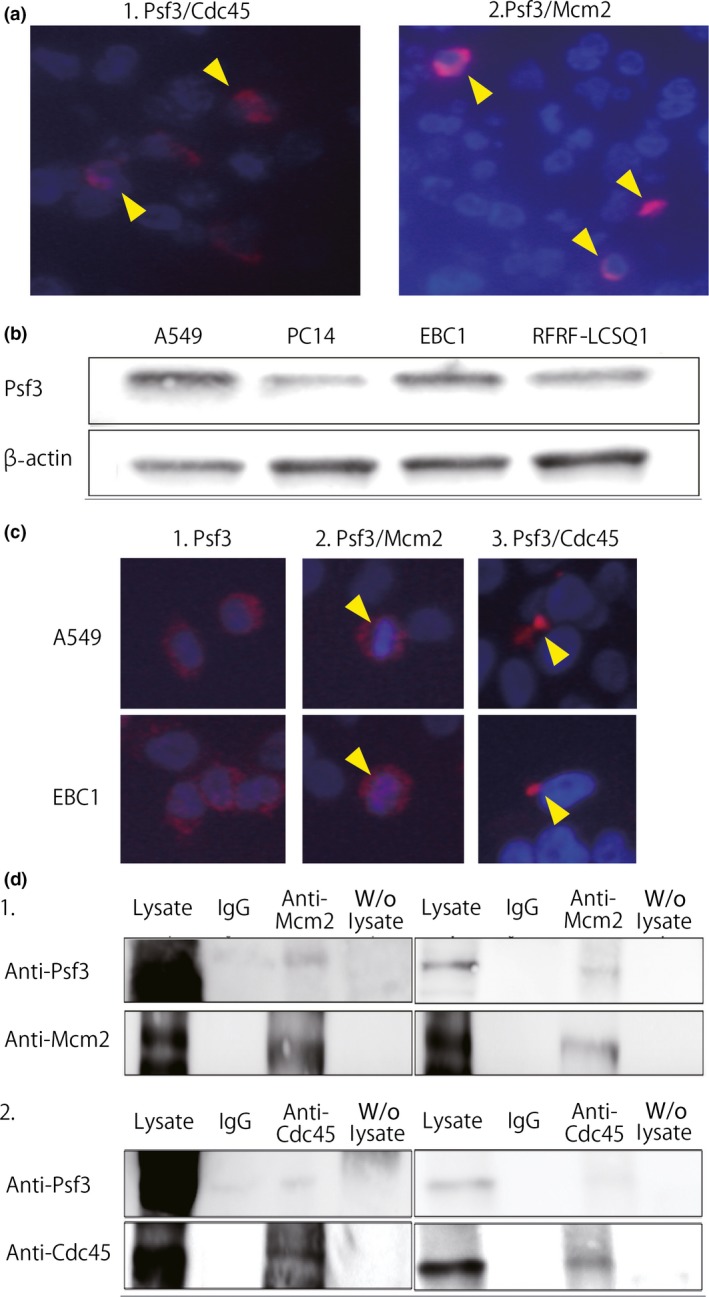
(a) Proximal ligation assay showed interactions between Psf3 and other Cdc45–Mcm–GINS (CMG) components, such as Cdc45 (a‐1) and Mcm2 (a‐2), in non‐small‐cell lung cancer specimens (arrowheads). (b) Western blotting for Psf3 and β‐actin in lung adenocarcinoma cell lines A549 and PC14 and lung squamous cell carcinoma cell lines RFRF‐LCSQ1 and EBC1. We detected strong expression of Psf3 in A549 and EBC1. (c) Immunofluorescent staining for Psf3 expression in A549 and EBC1 cells. DNA was counterstained with DAPI (blue). Nuclear accumulations of Psf3 were observed with a diffuse pattern in both cell lines (red). Proximal ligation assay analysis of the interaction between Psf3 and Mcm2. In both A549 and EBC1, dual protein interactions were observed in a portion of the Psf3‐positive cells, located around the nuclei. Interactions between Psf3 and Cdc45 were also observed in both cell lines. (d) Lysates from A549 and EBC1 cells were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti‐Mcm2 and anti‐Cdc45 antibodies. The precipitates were separated by SDS‐PAGE followed by immunoblotting with anti‐Psf3, anti‐Mcm2, and anti‐Cdc45 antibodies. In both cell lines, Psf3‐positive signals were clearly detected in anti‐Mcm2 and anti‐Cdc45 precipitates.
