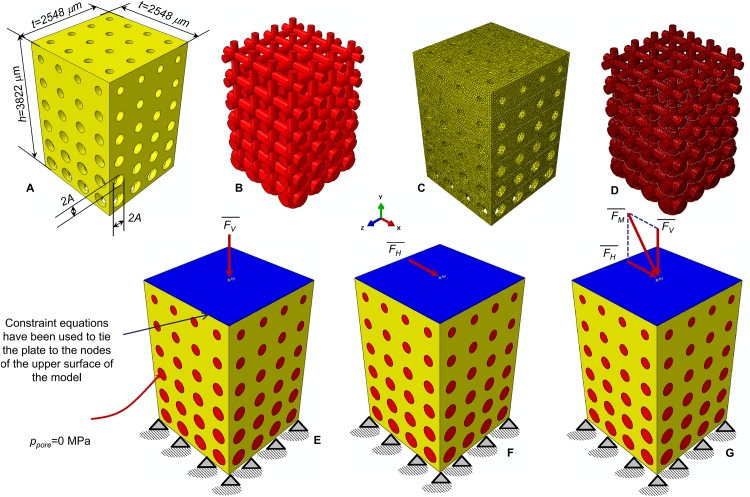
Fig 1. Parametric finite element model of the functionally graded scaffold utilized in the study.
CAD model (A-B) and finite element mesh (C-D) of the scaffold (A, C) and granulation tissue (B, D). Circular pores with variable radius A have been modelled. The nodes of the bottom surface of the model were clamped (E-G) while those of the upper surface were tied to a rigid plate (represented in blue). Three different loading conditions were hypothesized: a compression force (E); a shear force (F); a mixed compression-shear force (G). The pore pressure ppore on the outer surfaces of the granulation tissue was set equal to zero to simulate the free exudation of fluid.