Abstract
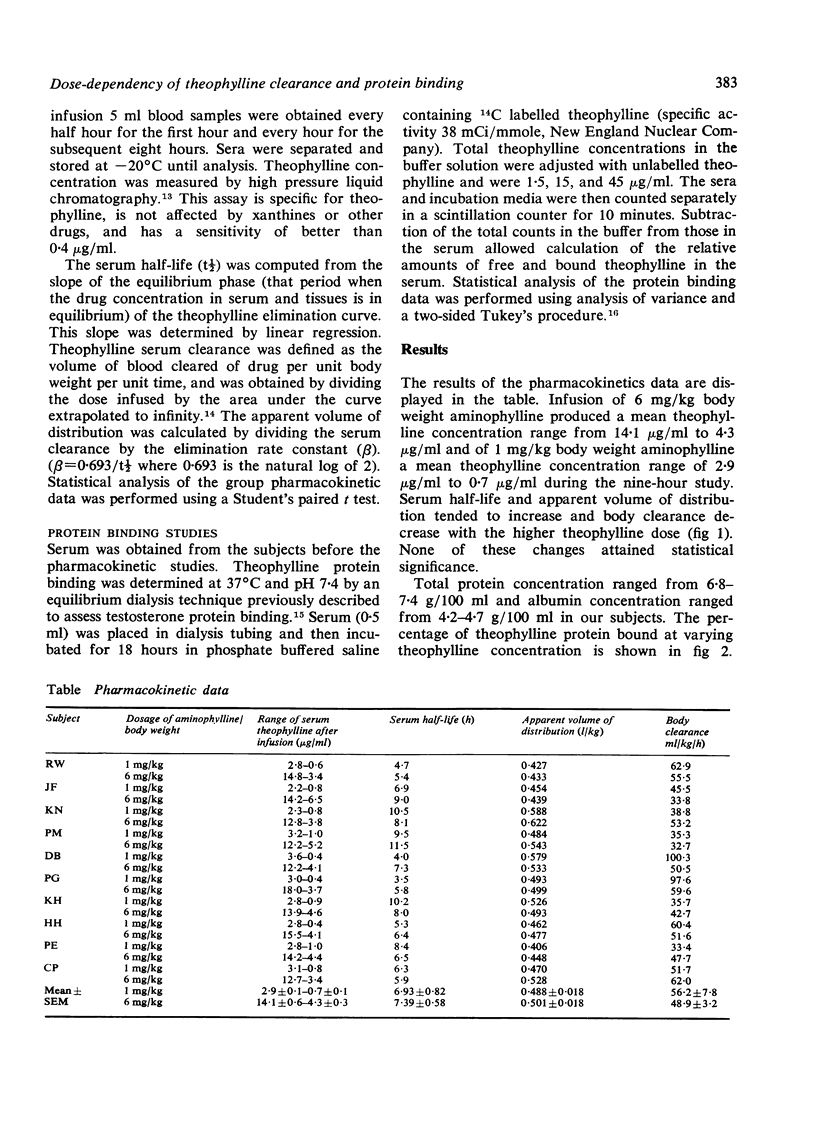
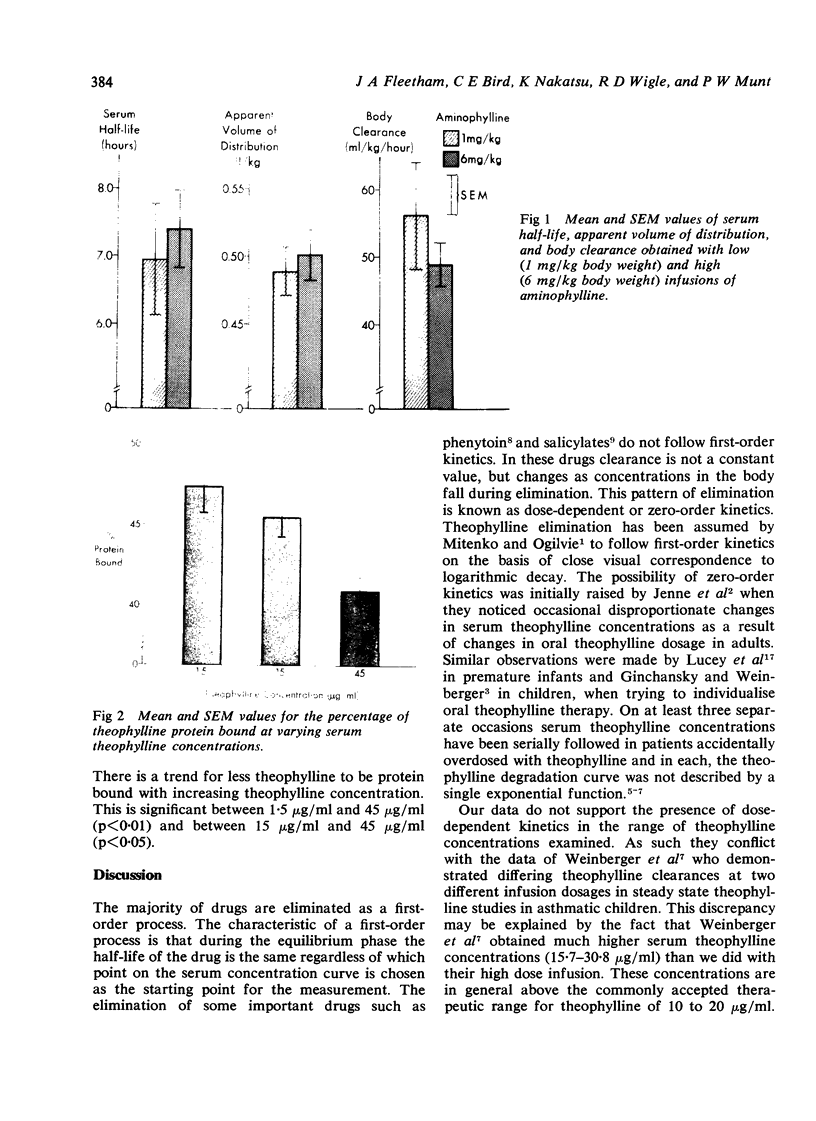
Dose-dependency in theophylline pharmacokinetics and protein binding characteristics was examined in 10 healthy male volunteers. Theophylline disposition was determined after an intravenous infusion of both 1 mg/kg and 6 mg/kg aminophylline in a randomised crossover study. There was considerable intrasubject variability in theophylline clearance but no significant dose-dependency. Theophylline protein binding was assessed by equilibrium dialysis at varying theophylline concentrations. The percentage of free non-protein bound theophylline was significantly increased at high theophylline concentrations. This increase in free theophylline would lead to a non-linear increase in the risk of toxicity with increasing drug concentration.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aranda J. V., Sitar D. S., Parsons W. D., Loughnan P. M., Neims A. H. Pharmacokinetic aspects of theophylline in premature newborns. N Engl J Med. 1976 Aug 19;295(8):413–416. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197608192950803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleetham J. A., Ginsburg J. C., Nakatsu K., Wigle R. D., Munt P. W. Resin hemoperfusion as treatment for theophylline-induced seizures. Chest. 1979 Jun;75(6):741–742. doi: 10.1378/chest.75.6.741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillette J. R. Overview of drug-protein binding. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1973 Nov 26;226:6–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1973.tb20464.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginchansky E., Weinberger M. Relationship of theophylline clearance to oral dosage in children with chronic asthma. J Pediatr. 1977 Oct;91(4):655–660. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)80527-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gugler R., Manion C. V., Azarnoff D. L. Phenytoin: pharmacokinetics and bioavailability. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1976 Feb;19(2):135–142. doi: 10.1002/cpt1976192135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendeles L., Weinberger M., Bighley L. Disposition of theophylline after a single intravenous infusion of aminophylline. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Jul;118(1):97–103. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.118.1.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenne J. W., Wyze M. S., Rood F. S., MacDonald F. M. Pharmacokinetics of theophylline. Application to adjustment of the clinical dose of aminophylline. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1972 May-Jun;13(3):349–360. doi: 10.1002/cpt1972133349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadlec G. J., Jarboe C. H., Pollard S. J., Sublett J. L. Acute theophylline intoxication. Biphasic first order elimination kinetics in a child. Ann Allergy. 1978 Dec;41(6):337–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch-Weser J., Sellers E. M. Binding of drugs to serum albumin (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1976 Feb 5;294(6):311–316. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197602052940605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy G., Tsuchiya T. Salicylate accumulation kinetics in man. N Engl J Med. 1972 Aug 31;287(9):430–432. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197208312870903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitenko P. A., Ogilvie R. I. Pharmacokinetics of intravenous theophylline. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1973 Jul-Aug;14(4):509–513. doi: 10.1002/cpt1973144part1509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakatsu K., Owen J. A., Scully K. Reliable fifteen-minute assay for theophylline. Clin Biochem. 1978 Aug;11(4):148–149. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9120(78)90332-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson D. P., Chick T. W. A re-evaluation of parenteral aminophylline. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1973 Aug;108(2):241–247. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1973.108.2.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogilvie R. I. Clinical pharmacokinetics of theophylline. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1978 Jul-Aug;3(4):267–293. doi: 10.2165/00003088-197803040-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piafsky K. M., Sitar D. S., Rangno R. E., Ogilvie R. I. Theophylline disposition in patients with hepatic cirrhosis. N Engl J Med. 1977 Jun 30;296(26):1495–1497. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197706302962603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallner J. J. Binding of drugs by albumin and plasma protein. J Pharm Sci. 1977 Apr;66(4):447–465. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600660402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallner J. J., Speir W. A., Jr, Kolbeck R. C., Harrison G. N., Bransome E. D., Jr Effect of pH on the binding of theophylline to serum proteins. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Jul;120(1):83–86. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.120.1.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner J. G. A modern view of pharmacokinetics. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1973 Oct;1(5):363–401. doi: 10.1007/BF01059664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walson P. D., Strunk R. C., Taussig L. M. Intrapatient variability in theophylline kinetics. J Pediatr. 1977 Aug;91(2):321–324. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)80844-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger M., Ginchansky E. Dose-dependent kinetics of theophylline disposition in asthmatic children. J Pediatr. 1977 Nov;91(5):820–824. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)81051-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- du Souich P., McLean A. J., Lalka D., Erill S., Gibaldi M. Pulmonary disease and drug kinetics. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1978 Jul-Aug;3(4):257–266. doi: 10.2165/00003088-197803040-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




