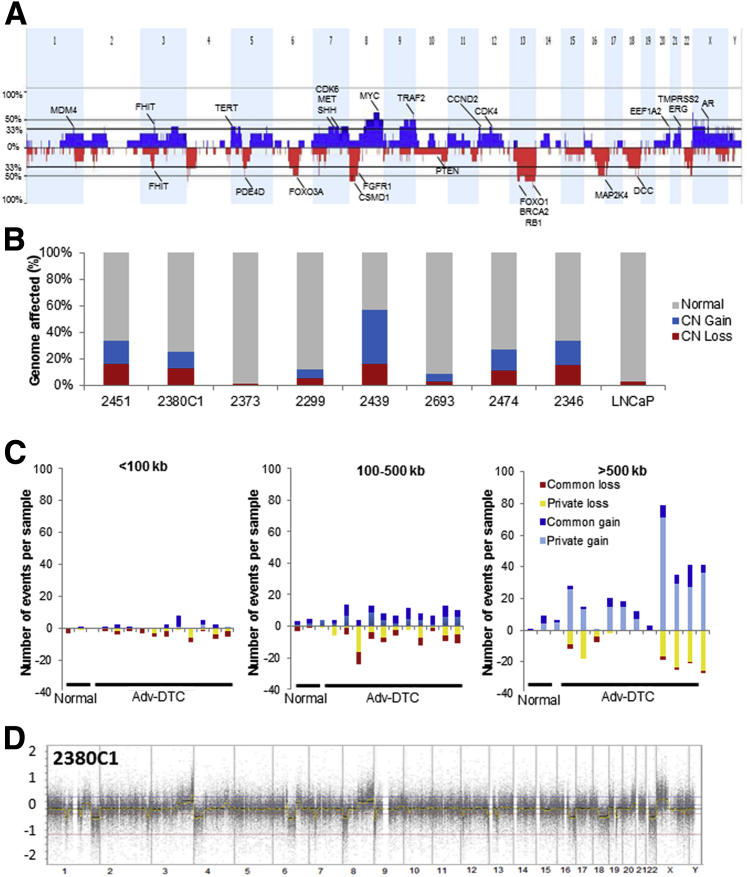
Figure 3.
Genomic profiles of DTC from patients with advanced prostate cancer show highly aberrant genomes. A: Combined genome profile of the eight Adv-DTCs from eight different patients, with selected genes of interest highlighted. B: Individual genomic profile results for the eight patients. The x axis indicates the patient case number or cell line. y axis indicates the percentages of genome of each sample that is normal (gray), CN gain/amplification (blue), and CN loss (red). The cell numbers in the samples were 20 cells for patient 2451, 20 cells for patient 2380C1, 10 cells for patient 2373, 10 cells for patient 2299, 13 cells for patient 2439, 5 cells for patient 2693, 10 cells for patient 2474, and 20 cells for patient 2346. The bulk LNCaP DNA result is shown on the far right. C: The distribution of size and type of CNAs in DTCs relative to normal and tumor samples. Dark bars indicate CN variations that are common among the population, whereas yellow and light blue indicate CNAs that are considered private and likely to be tumor specific. Normals include CD45+ lymphocytes from the blood or bone marrow. D: A representative DTC profiling (2380C1) is shown. Adv, advanced; CN, copy number; CNA, copy number aberration; DTC, disseminated tumor cell.